Mesalamine"Generic mesalamine 400 mg fast delivery, medications with dextromethorphan". By: S. Rozhov, M.B.A., M.D. Program Director, Stanford University School of Medicine Obstetrics & Gynecology Books Full 10 Endoscopy: Hysteroscopy and Laparoscopy paracervical block with 1% lidocaine symptoms 0f pneumonia purchase 800mg mesalamine with visa. Liberal use of paracervical block in difficult procedures allows the physician to be successful in obtaining endometrial biopsy tissue in more than 95% of cases, so this is likely true for hysteroscopy as well. Subsequently, the cervix can be dilated with tapered plastic or metal dilators, and the hysteroscopy can be completed. Unlike with larger rigid scopes, most patients will not require anesthesia for diagnostic procedures in the office. The infusion line should be flushed through the scope prior to insertion; otherwise bubbles will be introduced and obscure the view. When inserting the hysteroscope, it is useful to wait a few seconds to let the distending media open the internal cervical os so that the uterine cavity can be entered more easily by following the fluid flow. This point must be remembered in the context of viewing an anteverted versus retroverted uterus. If uterine cavity vision is obscured, it may be due to insufficient distention fluid, bleeding, or being up against the uterine wall or pathology. Never advance the hysteroscope without good visualization because perforation can occur. First, an overall view can be seen on entry looking for the general cavity shape, polyps, myomas, and foreign bodies. As the hysteroscope is advanced, it is rotated clockwise and counterclockwise to see the cornua and tubal ostia. Overzealous cervical dilation can create a poor seal between the cervix and scope, allowing the fluid to run out of the cervix and poor uterine distention. Vaginal and oral misoprostol (prostaglandin E1) given the night before the procedure, in dosages of 200 to 800 mcg can aid in the transcervical passage of the hysteroscope. This can be useful for women at risk for cervical stenosis such as those with prior cervical surgery and nulliparous women. In postmenopausal women, pretreatment with vaginal estrogen for 2 weeks before Table 10. Women should be warned of the side effects of misoprostol, including diarrhea, cramping, uterine bleeding, and fever. For more involved procedures, intravenous analgesia and conscious sedation may be needed, and proper protocols are needed to ensure patient safety. If extensive resections are anticipated via hysteroscopy, then the procedure is better performed on an outpatient basis in the surgical suite. For the severely stenotic cervix, having the right instruments available is critical. Lacrimal duct dilators (from ophthalmologic surgery) come in graduated sizes down to 1 mm in diameter. This can lead to cervical access when barely a dimple is seen in the external cervical os. Then, the usual tapered metal or plastic cervical dilators can facilitate complete dilation. Also, real-time ultrasonography can help the surgeon to visualize the tip of the dilator, direct the surgeon along the right track into the endometrial cavity, and prevent the surgeon from making a false cervical path or uterine perforation. Endoscopic procedures have progressed from snaring small polyps to hysteroscopic tubal sterilization, complex myomectomies, and ablating the entire endometrial lining. The ability to detect, biopsy, or remove focal lesions is extremely useful for abnormal bleeding workup over blind endometrial sampling. Approximately 50% of all Essure hysteroscopic tubal occlusions performed in the United States are done in an office setting, and the percentage is rising. Operative hysteroscopy may be performed with mechanical devices such as small operating scissors, electrocautery, and modified resectoscopes and lasers. With the development of the second-generation technology for uterine ablation and polyp and fibroid resection, the laser and resectoscope equipment is significantly less popular and less advantageous than simpler techniques. Women with repetitive miscarriages should have a diagnostic hysteroscopic procedure, which often leads to an operative procedure. Congenital abnormalities that interfere with the success of early pregnancies, such as septa of the uterus, may be seen and removed. Often endometrial polyps or submucous myomas are discovered and may be removed with a resectoscope wire.
Because the anomaly is asymptomatic and inconsequential medicine cabinet shelves 800mg mesalamine with amex, treatment should be undertaken only if there is a significant cosmetic problem. ErrichettiE,etal: Areolar sebaceous hyperplasia associated with oral and genital Fordyce spots. The ostia of the mucous ducts appear as red pinpoints surrounded by milky-white, slightly umbilicated, asymptomatic papules. The intervening mucosa becomes white and thick and tends to desquamate in places, leaving raw, beefy-red areas. Stomatitis nicotina is attributed to heavy smoking in middle-age men, although it has also been reported in nonsmokers who habitually drink hot beverages. Indeed, the most severe cases are associated with the type of tobacco use that produces intense heat- pipe and reverse smoking. Treatment consists of abstaining from the use of tobacco or the ingestion of hot liquids. Exostoses also frequently occur in the floor of the mouth, involving the inner surface of the mandible. Fissured tongue is seen in Melkersson-Rosenthal syndrome and in many patients with Down syndrome. Individual case reports have been seen in association with pachyonychia congenita, pemphigus vegetans, and Cowden syndrome. Geographic tongue occurs together with fissured tongue in 50% of patients, and both are more often present in psoriasis patients than nonpsoriatic patients. The condition gives rise to no difficulty, and treatment is not necessary, except that the deep furrows should be kept clean by use of mouthwashes. Herpetic geometric glossitis may mimic fissured tongue, but it is painful, affects predominantly immunocompromised individuals, and is centered on the back of the dorsal tongue. Geographic tongue is also known as lingua geographica, transitory benign plaques of the tongue, glossitis areata exfoliativa, and benign migratory glossitis. Geographic tongue begins with a small depression on the lateral border or the tip of the tongue, smoother and redder than the rest of the surface. This spreads peripherally, with the formation of sharply circumscribed, ringed or gyrate, red patches, each with a narrow, yellowish white border, making the tongue resemble a map. The appearance changes from day to day; patches may disappear in one place and manifest in another. The condition is frequently unrecognized because it produces no symptoms except for the occasional complaint of glossodynia. In one type, discrete, annular "bald" patches of glistening, erythematous mucosa with absent or atrophic filiform papillae are noted. Another type shows prominent circinate or annular, white raised lines that vary in width up to 2 mm. The clinical appearance and histopathologic findings of the tongue lesions in pustular psoriasis, reactive arthritis (Reiter syndrome), and geographic tongue are identical; when the tongue lesions occur with psoriasis or reactive arthritis, the name annulus migrans has been suggested for this entity. Histologically, the main features are marked transepidermal neutrophil migration with the formation of spongiform pustules in the epidermis and an upper dermal mononuclear infiltrate. The "hairs" result from a benign hyperplasia of the filiform papillae of the anterior two thirds of the tongue, resulting in retention of long, conical filaments of orthokeratotic and parakeratotic cells. Black hairy tongue may be associated with several conditions that may be predisposing factors in its causation: smoking, use of oral antibiotics, xerostomia, psychotropic drugs, and presence of Candida on the surface of the tongue. Hairy leukoplakia is usually seen on the lateral surface of the tongue, at first in corrugated patches, then with time, as solid white plaques that are adherent. Such predisposing local factors as smoking, antibiotics, and oxidizing agents should be eliminated, if possible, and scrupulous oral hygiene maintained. Atrophic glossitis is also a distinctive sign of pellagra; it results from a deficiency of niacin or its precursor, tryptophan. It is the cleft distal to the vagina between the labia minora that is visualized when the labia are held apart treatment 1st degree av block purchase mesalamine pills in toronto. The orifices of the urethra and vagina and the ducts from Bartholin glands open into the vestibule. Within the area of the vestibule are the remnants of the hymen and numerous small mucinous glands. The mucosa of the proximal two thirds of the urethra is composed of stratified transitional epithelium, whereas the distal one third is stratified squamous epithelium. The distal orifice is 4 to 6 mm in diameter, and the mucosal edges grossly appear everted. The skin of the labia minora is less cornified and has many sebaceous glands but no hair follicles or sweat glands. The labia minora and the breasts are the only areas of the body rich in sebaceous glands but without hair follicles. Among women of reproductive age, there is considerable variation in the size of the labia minora. The labia minora are homologous to the penile urethra and part of the skin of the penis in males. Usually Skene ducts run parallel to the long axis of the urethra for approximately 1 cm before opening into the distal urethra. Skene glands are the largest of the paraurethral glands; however, many smaller glands empty into the urethra. The duct from each gland is lined by transitional epithelium and is approximately 2 cm in length. The intertriginous areas of the vulva remain moist, and obese women are particularly susceptible to chronic infection. The vulvar skin of a postmenopausal woman is sensitive to topical cortisone and testosterone but insensitive to topical estrogen. Chronic infections of the periurethral glands may result in one or more urethral diverticula. The most common symptoms of a urethral diverticulum are similar to the symptoms of a lower urinary tract infection: urinary frequency, urgency, and dysuria. The richness of the vascular supply and the absence of valves in vulvar veins contribute to this complication. The abundant vascularity of the region promotes rapid healing, with an associated low incidence of wound infection in episiotomies or obstetric tears of the vulva. The subcutaneous fatty tissue of the labia majora and mons pubis are in continuity with the fatty tissue of the anterior abdominal wall. Infections in this space such as cellulites and necrotizing fasciitis are poorly contained and may extend cephalad in rapid fashion. The walls of the vagina are normally in apposition and flattened in the anteroposterior diameter. The axis of the upper portion of the vagina lies fairly close to the horizontal plane when a woman is standing, with the upper portion of the vagina curving toward the hollow of the sacrum. In most women an angle of at least 90 degrees is formed between the axis of the vagina and the axis of the uterus. The vagina is held in position by the surrounding endopelvic fascia and ligaments. The lower third of the vagina is in close relationship with the urogenital and pelvic diaphragms. The middle third of the vagina is suspended by the lower portion of the cardinal ligaments and supported by the levator ani muscles. The upper third is suspended by the upper portions of the cardinal ligaments and the parametria. The vagina of reproductive-age women has numerous transverse folds, vaginal rugae. They help provide accordion-like distensibility and are more prominent in the lower third of the vagina. The posterior fornix is considerably larger than the anterior fornix; thus the anterior vaginal length is approximately 6 to 9 cm in comparison with a posterior vaginal length of 8 to 12 cm. If the environment of the vaginal mucosa is modified, as in uterine prolapse, then the epithelium may become keratinized. The squamous epithelium is similar microscopically to the exocervix, although the vagina has larger and more frequent papillae that extend into the connective tissue. Order mesalamine canada. Pneumonia Pathological Causes Symptoms H/Dr Minhas = نمونیہ وجوہات علامات علاج.
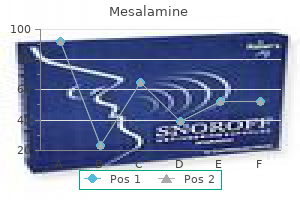
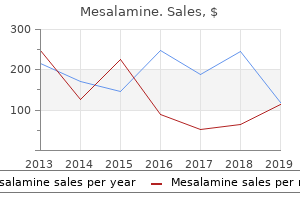
Syndromes
Hymens in newborns are estrogenized symptoms quitting weed purchase mesalamine 400mg visa, resulting in a pink thick elastic redundancy. Older unestrogenized girls will have thin nonelastic hymens with significant signs of vascularity. The vaginal epithelium of the prepubertal child appears redder and thinner than the vagina of a woman in her reproductive years. The vagina is 4 to 6 cm long, and the secretions in a prepubertal child have a neutral or slightly alkaline pH. Recurrent vulvovaginitis, persistent bleeding, suspicion of a foreign body or neoplasm, and congenital anomalies may be indications to perform vaginoscopy and examine the inside of the vagina. Vaginoscopy in a prepubertal child most often requires sedation with a brief inhalation or intravenous anesthetic, but it can also be performed in the office with older, cooperative children in select circumstances. The introduction of any instrument into the vagina of a young child takes skillful patience. The prepubertal vagina is narrower, thinner, and lacks the distensibility of the vagina of a woman in her reproductive years. There are many narrow-diameter endoscopes that will suffice, including the Kelly air cystoscope, contact hysteroscopes, pediatric cystoscopes, smalldiameter laparoscopes, plastic vaginoscopes, and special virginal speculums designed by Huffman and Pederson. The ideal pediatric endoscope is a cystoscope or hysteroscope because the accessory channel facilitates the retrieval of foreign bodies as well as vaginal lavage. Local anesthesia of the vestibule may be obtained with 2% topical viscous lidocaine (Xylocaine) or longer-acting products such as lidocaine/prilocaine. A complete vaginal evaluation should never be performed under duress or by force, frequently the reason to use sedation when performing this examination on children. Common reasons to perform a rectal examination include genital tract bleeding, pelvic pain, and suspicion of a foreign body or pelvic mass. The child should be warned that the rectal examination will feel similar to the pressure of a bowel movement. The critical factors surrounding the pelvic examination of a female adolescent are different from those of examinations of children 2 to 8 years old. Many female adolescents do not want their mother, guardian, or other observers in the examining room. In many adolescent gynecology visits, a full pelvic exam is unnecessary (Lara-Torre, 2008). Each adolescent is at a different stage of development, and the approach to the exam may require variations that fit her developmental stage. A patient in early adolescence (12 to 14 years of age) may behave and need similar support as those in the prepubertal stages. They may ask for their mothers to be there, be fearful of the examination concept, and need more than one visit to achieve the goals of the visit. Adolescents often come for examinations with preconceived ideas that it will be very painful. Slang terminology for speculums among teens includes the threatening label "the clamp. Providers can counsel patients that they will inform them of each step in the process and then ask the teen if she is ready before performing each step. This places the teen in control of the tempo and allows her to anticipate the next element of the examination. Allowing them to see and touch the instruments also may assist in demystifying the exam and allow for it to flow more smoothly. The examiner provides pressure lateral to the introitus on the perineum prior to insertion of the speculum. It is estimated that 80% to 90% of outpatient visits of children to gynecologists involve the classic symptoms of vulvovaginitis: introital irritation (discomfort/pruritus) or discharge (Table 12. With puberty the prepubertal vagina becomes acidic under the influence of bacilli dependent on a glycogenated estrogen-dependent vagina.
|