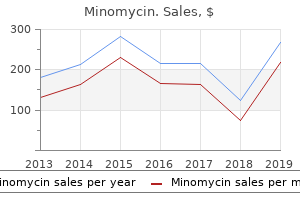
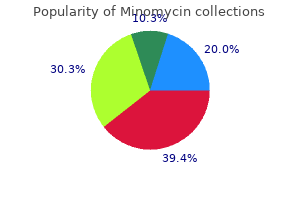
Minomycin"Cheap minomycin line, infection games online". By: L. Brontobb, M.B.A., M.B.B.S., M.H.S. Medical Instructor, University of Iowa Roy J. and Lucille A. Carver College of Medicine These aneurysms are protrusions that do not have the elastic and muscular layers typical for arteries infection 8 weeks after giving birth cheap minomycin online. Cerebral G (a) of the carotid artery shows a sack of aneurysm heterogeneously filled with contrast medium (arrow). These aneurysms fall into two categories: (1) as a result of penetrating injury; and (2) as a result of non-penetrating injury. The most likely cause for the aneurysms of the penetrating injury is gunshot wounds to the skull. According to the statistical data, up to 50% of all patients with this type of injury have saccular aneurysms. However, early diagnosis is complicated by the presence of the huge foci of brain tissue damage and haemorrhage. The penetrating injury of extracranial vessels can be the cause of arterial and arteriovenous fistula, dissection and traumatic pseudo-aneurysms. Pseudo-aneurysms or false aneurysms are cavities inside of the blood clot that surrounds the artery. Such a cavity is connected with the arterial lumen, and it does not have any layers typical for the arterial wall. Aneurysms that are consequences of non-penetrating injury are usually located at the skull base, and they are mainly caused by the fracture of bones of skull base adjacent to vessels. Closed craniocerebral injury can cause the formation of aneurysms on the peripheral (distal, towards the arterial circle of cerebrum) arteries. There were reports about aneurysm formation on the pericallosal artery after the injury caused by the low edge of the falx cerebri. Aneurysm (c,d) of the left superior cerebellar artery (arrow) Cerebrovascular Diseases and Malformations of the Brain 205. Such process starts from internal vessel surface and goes towards the external surface. Infectious process penetrates the vasa vasorum system and gradually affects all layers including adventitia, which at the end leads to the weakening of the wall and subsequent aneurysm formation. The most frequent location is a thoracic aorta; the involvement of intracranial vessels is observed much more rarely. They are caused by the tumoral invasion of the arterial wall, with the consequent protrusion of the affected wall. There are reports about the findings of aneurysms in patients with the malignant glioma, pituitary adenoma and choroid carcinoma. The majority of them are characterised by the presence of the increased mobility, skin hyperelasticity and damage with the formation of the pathological scars. Collagen is a main component of elasticity for structures such as arteries and veins, and also walls of intestines and visceral organs. Presumably, it plays a role in maintenance of the structural integrity of a connective tissue. They are diagnosed at least in first-degree relatives, and they are not related to any other known hereditary form of connective tissue diseases. Microscopic examination of vessel walls in patients with this form of disease reveals signs of antipathy, with damage to both extra- and intracranial vessels. It is inherited as an autosomal-dominant type; however, features of the disease can be absent in 30% of relatives. As a rule, arterial aneurysms in these patients are saccular, fusiform or dissecting. Intracerebral haemorrhage in the right temporal lobe due to rupture of arterial aneurysm of the middle cerebral artery. Large hypodense area within the internal carotid artery area, dislocation of the ventricular system and signs of tentorial impaction are seen along with the absence of the circumferential cistern. Dislocation of the ventricular system, small amount of blood in the posterior horn of the lateral ventricle. Intracerebral haemorrhages can, however, be easily revealed even after several weeks since the subarachnoid haemorrhage, as areas of decreased density. Thus, it is necessary to note that the degree of such a narrowing in many aspects depends on location of haemorrhage and the amount of extravasated blood. In the rest of the patients antibiotic resistance in bacteria is the result of buy minomycin online pills, causes of fatal outcome were different extracranial complications like septic pneumonia, myocardial infarction, pulmonary embolism etc. Interpeduncular cistern may be poorly visualised due to small quantities of isodensive blood. Acute obstructive hydrocephalus may develop within the first week due to ependymitis or intraventricular blood occluding the Sylvian aqueduct or the fourth ventricle. Communicating hydrocephalus may develop within the first hours at first week if arachnoid granulations are filled with blood, thus leading to fibroplastic proliferation in subarachnoid spaces and their blockage. Intracerebral haematomas may cause white matter tracts damage, with blood rupture into the ventricular system. Hypointense signal at haematoma periphery means accumulation of haemosiderin (the beginning of chronic phase). If these two injuries are isolated and hydrocephalus is absent, then they are clinically insignificant. As a rule, pneumocephalus is not life threatening because air is gradually absorbed. Sometimes air volume may increase due to valve mechanism producing tense pneumocephalus, which often occurs after skull base fractures, and after craniotomy. Pneumocephalus is usually marked soon after trauma; however, it may develop days or months later. Epidural air is frequently located in the same place and does not move when the head changes position. Intraventricular air is usually identified in the anterior horns of lateral ventricles and intraventricular blood, conversely, is often found in the posterior horns. Tense pneumocephalus and pneumocele sometimes require immediate surgical treatment if patient condition deteriorates. On the other hand, one third of patients with severe head injuries do not have fractures. Nevertheless, due to wide accessibility (any hospital has an X-ray device) and legal reasons, this diagnostic tool is widely used. Bone damages are significant not only as signs of trauma itself, but also as way of infectious dissemination, when fracture is accompanied by loss of integrity of adjacent tissues. While healing, the line of fracture can be hardly distinguished from such structures like vascular picture or bone sutures. Depending on location, skull fractures are subdivided onto skull vault fractures and skull base fractures. Gunshot (injuries) fractures form a separate group, for they significantly differ from civil injuries. Several authors also distinguish whole fractures (fractures with bone defect formation). Linear fractures occur with blunt injury, they are more vivid than the vascular picture, and cranial sutures have different configuration and length, rectification and angularity, sharpness and clarity of visualisation, and frequently, separated visualisation of fissures in the internal and external cranial bone lamina fractures is had. Linear fractures are frequently located in the parietotemporal, frontal, and occipital regions and tend to expand from the cranial vault to the skull base. Special attention is required if a linear fracture crosses the sulci of meningeal arteries, venous sinuses and channels of the diploetic veins. In unclear cases, target (contact) craniography is required to ascertain the size and precise location of fracture. If fracture line does not heal, then leptomeningeal cysts or meningoencephalocele may develop. Both complications occur due to complex fracture with rupture of dura mater and invagination of soft tissues between fragments of fractured bones. Brain pulsation is transmitted into margins of bone defect, hampers healing and leads to its dilatation. In contrast to linear fractures, impacted ones are not so clearly visualised, which is why in all cases when they are suspected, it is necessary to perform target (tangential and contact) craniography. In the former there is no complete divergence of bone fragments, and the integrity of the internal cranial bone lamina is preserved at the periphery of traumatic lesion. If the square of impaction does not exceed thickness of adjacent skull vault bones, then damage of dura mater rarely occurs. Generic minomycin 50 mg fast delivery. How to Get Rid of Warts Naturally.
Neuraxial blockade of nociceptive stimuli by epidural and spinal local anesthetics has been shown to blunt the metabolic and neuroendocrine stress response to surgery antimicrobial toilet seats discount minomycin 50mg with amex. To be effective, the blockade must be established before incision and continued postoperatively. However, the advantages of neuraxial blockade are not as evident when minimally invasive surgical techniques are used. Lumbar epidural anesthesia/analgesia should be discouraged for abdominal surgery because it often does not provide adequate segmental analgesia for an abdominal incision. By sparing opioid use and minimizing the incidence of systemic opioid-related side effects, epidural analgesia facilitates earlier mobilization and earlier resumption of oral nutrition, expediting exercise activity and attenuating loss of body mass. Neural blockade minimizes postoperative insulin resistance, attenuating the postoperative hyperglycemic response and facilitating utilization of exogenous glucose, thereby preventing postoperative loss of amino acids and conserving lean body mass. If spinal anesthesia is used for fast-track (and especially ambulatory) surgery, attention must be paid to delayed recovery due to prolonged motor blockade. The introduction of ultrashort-acting intrathecal agents such as 2-chloroprocaine (still controversial at present) may further speed the fast-track process. Spinal opioids are associated with side effects such as nausea, pruritus, and postoperative urinary retention. Adjuvants such as clonidine are effective alternatives to intrathecal opioids, with the goal of avoiding untoward side effects that may delay hospital discharge. Further studies are needed to define the safety and efficacy of regional anesthesia techniques in fast-track cardiac surgery (and many clinicians avoid them due to concerns about neuraxial hematomas). Although some studies have shown that spinal analgesia with intrathecal morphine decreases extubation time, decreases length of stay in the intensive care unit, reduces pulmonary complications and arrhythmias, and provides analgesia with less respiratory depression, other studies have shown no benefit to this approach. The choice of local anesthetic, dosage, and concentration should be made with the goal of avoiding prolonged motor blockade and delayed mobilization and discharge. Ropivacaine, because of its lower toxicity relative to bupivacaine, is often preferred when high volumes of local anesthetic solution are needed. Efforts must be made to minimize the motor block of the quadriceps, which can be responsible for accidental falls. Administering a lumbar plexus block along with a sciatic nerve block decreases hospital length of stay, postoperative urinary retention, and ileus associated with lower extremity total joint replacement when compared with general or neuraxial anesthesia followed by intravenous opioids. The same benefits of fewer opioid side effects and accelerated discharge have been shown with regional anesthesia/analgesia for hand, shoulder, anorectal, and inguinal hernia repair surgery. Advances in imaging techniques and peripheral catheter technology have generated interest in abdominal wall blockade, facilitating the selective localization of nerves and the direct deposition of local anesthetic in proximity to the compartments where the nerves are located. These techniques are alternatives to epidural blockade when the latter is contraindicated. In patients undergoing colorectal and radical retropubic prostate surgeries, intravenous lidocaine has been shown to reduce requirements for opioids and general anesthetic agents, to provide satisfactory analgesia, to facilitate early return of bowel function, and to accelerate hospital discharge. The most effective dose and duration of infusion for various surgical procedures remains to be determined; even short duration of lidocaine infusion may have benefit. They also have been shown to prevent perioperative cardiovascular events in at-risk patients undergoing noncardiac surgery and to help maintain hemodynamic stability during the intraoperative period and during emergence from anesthesia. Blockers reduce the requirement of volatile anesthetic agents and decrease minimum alveolar concentration values; they may also have an opioid-sparing effect. They possess anticatabolic properties, which may be explained by reduced energy requirements associated with decreased adrenergic stimulation. A positive protein balance has been reported in critically ill patients when blockade is combined with parenteral nutrition. Intravenous 2-Agonist Therapy Both clonidine and dexmedetomidine have anesthetic and analgesic properties. Clonidine decreases postoperative pain, reduces opioid consumption and opioid-related side effects, and prolongs neuraxial and peripheral nerve local anesthetic blockade. In patients undergoing cardiovascular fast-track surgery, spinal morphine with clonidine decreases extubation time, provides effective analgesia, and improves quality of recovery. Inhalational Anesthetics Compared with other volatile anesthetic agents, desflurane and sevoflurane can shorten anesthesia emergence, reduce length of stay in the postanesthesia care unit, and decrease recovery-associated costs. Nitrous oxide, because of its anesthetic- and analgesic-sparing effects, rapid pharmacokinetic profile, and low cost, is frequently administered with other inhalation agents. Blood should not be vigorously shaken lin reagent (of animal or monoclonal origin) or heated antibiotics for sinus infection how long to work order minomycin 50 mg line. Any evibody will then agglutinate, again indicating dence of hemolysis should be looked incompatibility. Catheterization to record the urine complications due to massive transfusion output and a close watch of the (see above). Fursemide 80 to 120 mg is given to provoke a diuresis and repeated if the immunologically mediated reactions the urine output falls below 30 ml may be directed against red or white blood per hour. The white cell antibodies in the recipient are formed as a result of previous transfusions or pregnancies. If they are troublesome in patients requiring further transfusions, leukocyte depleted blood may be given. It occurs as a result of incompatibility between donor antibodies and recipient granulocytes. On subsequent Immediate Hemolytic Transfusion Typically occurs 5 to 10 days after transfusion. Urticaria results from the allergic reacbecause of a clerical error in identification at renewed synthesis of antibody which may tion to plasma products in the donor the time the blood sample was drawn, during take a few hours to a few weeks to develop. It is treated by stopping Delayed Hemolytic Transfusion Reactions 21 Section 1 Physiological Basis of Surger y a. Congestive cardiac failure-This can due to anti-IgA formed as a result of preoccur if blood is transfused too rapidly vious transfusion in subjects who either especially in the elderly or when there lack IgA or who belong to a different IgA is cardiovascular insufficiency. At Infectious Complications the same time, the transfusion should be given slowly over a period of many the following infections can be transmitted hours. All patients requiring they have been punctured by a needle for multiple transfusions and all health care workadding some drug to the infusate. Therefore, if large volumes of this and 10 percent of patients, cirrhosis or stored blood are used, these factors may hepatoma. In these patients, blood must be filtered to remove the leukocytes which transmit the intracellular virus. It acts as an alternative to homologous endemic areas, travelers, who have recently transfusion with the advantages in safety and resided in an endemic area, are excluded from cost. A unit is taken each week and 500 ml of saline is infused to maintain the intravascular volume and 200mg of ferrous sulfate per day, started. Two to four units of blood are predeposited in this way, the final donation being made not less than 72 hours prior to surgery. Part I General Surgery Preoperative Isovolemic Hemodilution For some operations like cardiopulmonary bypass 1 to 2 units of blood may be withdrawn, just before surgery. This procedure not only restores much of the individuals red cells but also provides platelets. Peroperative Blood Salvage Blood is collected from the operation site, filtered to remove the cellular debris, activated clotting factors, etc. Vasoconstriction Immediately after injury, the first response designed to control hemorrhage is contraction of the blood vessel wall, which reduces the diameter of the vessel and thus the size of the opening. This spasm results from nervous reflexes (sympathetic activity), local myogenic spasm and local humoral factors from the traumatized tissues. This spasm serves to reduce the bleeding while platelets gather in the wound and the coagulation process is initiated. Vasoconstriction also occurs in response to Thromboxane A2, a product of arachidonic acid metabolism in platelet membranes. Platelet adhesion-Endothelial damage exposes blood to collagen and other aggregates them. The platelet has a recepping blood loss from capillaries, small artetor, called glycoprotein 1b on its surface rioles and venules whereas the third phase for the bound von Willebrand factor that of hemostasis (formation of solid fibrin) then serves as the bridge between subenrequires several minutes for completion. Receptor fibrin strands which are produced strengthen engagement activates the platelet. Granule release or platelet release reaction-Following activation there is flattenprevents recurrent bleeding hours or days ing of the adherent platelets on the damafter the initial injury. Several proteins including the von coagulation reaction, such as thrombin, Willebrand factor, fibronectin, thromstimulate platelet aggregation.
|