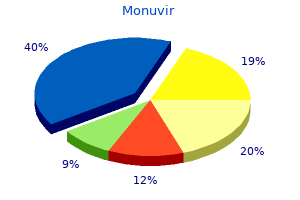
Monuvir"Buy monuvir cheap online, antivirus wiki". By: J. Milok, M.B. B.A.O., M.B.B.Ch., Ph.D. Clinical Director, Marist College One patient completed two normal pregnancies without relapse before a mild relapse occurred in a third pregnancy antiviral used to treat herpes buy monuvir with visa. Relapse did not occur in a patient with kidney transplant who was maintained on immunosuppression. Relapse affected the liver in one patient with stable renal function before pregnancy, and it resulted in fibrinoid necrosis of hepatic parenchyma and fetal loss (228). In a more recent survey of the literature, 28 pregnancies in patients with granulomatosis with polyangiitis were identified (229). The diagnosis of granulomatosis with polyangiitis was made during pregnancy in eight. Nineteen of 27 cases with outcomes recorded resulted in live births, 7 pregnancies terminated in abortions, and 2 maternal deaths occurred. Microscopic polyangiitis has only very rarely been reported in pregnancy (230), perhaps reflecting its lesser propensity to relapse than granulomatosis with polyangiitis. The baby showed an excellent clinical response to exchange transfusion and immunosuppression, and the mother also responded to therapy (231). The rapid decline of renal function postpartum was postulated to have been due in part to removal of the ameliorating influence of the placenta (232). An additional case of rapid decline in renal function postpartum has been described, although further studies were not performed in this case (233). Although individual case reports have described renal crisis during pregnancy, this condition does not appear to occur at an increased frequency during pregnancy (235,236). In amyloidosis, as in other renal diseases, more severely compromised renal function at conception was associated with deterioration of renal function during pregnancy (237). Kidney Transplant the effect of pregnancy on renal function in renal allografts has been studied in detail. No adverse effects of pregnancy on graft function were detected in a series of 113 pregnancies in 73 transplanted women (241). Premature delivery occurred in 64% of the pregnancies, with no congenital defects or renal functional defects, hypertension, or proteinuria observed in these babies, followed on average till age 52 months (242). In several large series, comparing matched male or nonpregnant female cohorts with transplant recipients who became pregnant, no adverse long-term effect on renal allograft function or survival was detected (238). Although creatinine clearance decreased late in pregnancy in renal transplant patients to a greater extent than in healthy women, permanent impairment of renal function was not typical. Proteinuria was also increased slightly during pregnancy, to approximately 200 mg/24 h versus 150 mg/24 h in normal subjects at comparable time of pregnancy. By the third trimester, proteinuria in renal transplant patients was three times that of nonpregnant levels, returning to prepregnancy levels by 2 to 3 months after delivery (1). In an additional case-control study, no significant difference was found in plasma creatinine levels after 15 years of follow-up (238). Patients with decreased renal function who also are receiving immunosuppression have decreased fertility. When renal transplant patients do conceive, spontaneous abortions are increased if significant renal insufficiency is present, whereas a good pregnancy outcome is associated with intact renal function (243). Renal Cancer the apparent increase in the number of cases of renal cancer in pregnancy may reflect increased incidental detection during pregnancy because of the routine use of ultrasound. Forty-four cases of renal cell carcinoma discovered during pregnancy were reported in one review (244). Formerly, palpable flank masses were the most common presentation, in contrast to early detection of smaller lesions with the use of high-resolution ultrasound. Parity was associated with increased risk for renal cancer in several cohort studies, but mechanism(s) and potential causality remain unclear (245). The most common agent of nocardiosis is Nocardia asteroides antivirus windows vista monuvir 200mg with visa, a filamentous bacteria present in nature. The bacteria are found in soils, and infection results from inhalation of infective forms or their introduction into soft tissue through trauma. Kidney involvement is rare and occurs as part of hematogenous dissemination, usually a pulmonary infection in immunocompromised patients (228) or in patients receiving corticosteroids. Renal infection results in single or multiple small abscesses or diffuse pyelonephritis, often with draining sinus tracts (229). Rickettsial Infections Rickettsial infections are transmitted through several vectors and are caused by obligatory intracellular microorganisms. All rickettsioses cause significant clinical disease, and most cause renal involvement, some with mild renal insufficiency and some with acute renal failure and fatal outcomes. Chapter 24 Pyelonephritis and Other Infections, Reflux Nephropathy, Hydronephrosis, and Nephrolithiasis 1067 roCky Mountain sPotted FeVer Rocky Mountain spotted fever, caused by Rickettsia rickettsii, is transmitted by bites of ticks. Patients present with fever, headache, myalgia, nausea, and vomiting, followed by a rash. Disseminated rickettsial infection causes increased vascular permeability, hypotension, and shock with prerenal azotemia. Some patients develop acute renal failure and, on biopsy, show inflammatory infiltration with mononuclear cells and neutrophils, edema, and tubular necrosis. The inflammation is more frequent around vessels and has a predilection for the outer medulla and corticomedullary junction. Although the diagnosis can be made by serologic tests, immunopathologic identification of Rickettsia in skin lesions is the only approach that results in a timely diagnosis of acute disease. Renal failure and tubulointerstitial nephritis may resolve or may contribute to death (230). Mediterranean sPotted FeVer Rickettsia conorii, the etiologic agent of Mediterranean spotted fever, also causes tubulointerstitial nephritis. In three patients, the kidneys showed multifocal perivascular tubulointerstitial nephritis. Renal involvement is infrequent and is comparable to that of other rickettsial infections but milder. Lymphohistiocytic inflammatory infiltrate is vasocentric, predominantly interstitial with associated edema and enlargement of tubular cells. Patients present with fever, myalgia, hypotension, petechiae, jaundice, proteinuria, hematuria, and pyuria (233). The interstitial mononuclear inflammatory infiltrate is vasocentric and forms typhus nodules. This patient was treated with doxycycline with improvement, but she developed acute renal failure 5 days after treatment was instituted. Her renal biopsy findings, 8 days after antibiotic treatment, demonstrated granulomatous tubulointerstitial nephritis. Continued treatment with doxycycline resulted in improvement of renal function and a decline in the titer of antibodies to R. More recently, several case reports and epidemiologic studies show that scrub typhus continuous to be not an infrequent problem for indigenous populations as well as travelers in Asia (235). Rickettsiae enter cells by receptor-mediated endocytosis through the cholesterol receptor. Injury to endothelial cells is mediated, at least in part, by superoxide radicals (235). Endothelial cells, smooth muscle cells, or both are infected, resulting in increased vascular permeability, vasculitis, thrombosis, and hemorrhages. Thrombosis appears to result from enhanced endothelial cell tissue factor expression and from release of von Willebrand factor from Weibel-Palade bodies. Patients present with renal dysfunction or acute renal failure and, in the case of Weil disease, jaundice. Humans acquire the microorganism when they are in direct contact with infected tissues or fluids or with contaminated water. Tubulointerstitial nephritis is the main pattern of renal injury in leptospirosis. 200mg monuvir overnight delivery. Antiretroviral Therapy Choice in HIV Infection.
Indian Root (American Spikenard). Monuvir.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96383 The kidneys are involved in one third of patients who die of disseminated infection (136) examples of antiviral drugs purchase cheapest monuvir and monuvir. Coccidioides immitis organisms are easily found in active lesions within macrophages or giant cells as thick-walled spherules, about 100 m in diameter, containing endospores that are 5 to 30 m in diameter (136). Disease progression has been equated with attenuation of cellular immunity from antigen overload, suppressor cells, immune complexes, and immunosuppressive factors released from the fungus. Containment of infection depends on cellular immunity that, through release of lymphokines, enhances phagosome-lysosome fusion and killing of the fungus as described above for other fungi. North American blastomycosis, caused by Blastomyces dermatitidis, is endemic in the Ohio and Mississippi River valleys and the southeastern United States (136). Primarily, a pulmonary infection disseminates through blood to various organs, including the kidneys. In severe infections, fever, weight loss, chest pain, cough, costovertebral angle tenderness, flank pain, renal insufficiency, and chronic discharging sinuses or subcutaneous abscesses have been reported. The diagnosis can be established through culture or by identifying the organism in fluids or tissue sections. Involvement is often bilateral and varies from small, circumscribed nodules to diffuse inflammation and necrosis (136). Perinephric abscesses and discharging sinuses may result from extension of the infection through the capsule. Occasional microabscesses and epithelioid caseating granulomas form, resembling tuberculosis. Blastomyces dermatitidis can be detected in either type of lesion as yeast cells with a double-contoured appearance. Although the presenting symptoms are usually pulmonary, the disease is often manifested by dissemination. Grossly, the renal cortex and medulla contain miliary necrotizing granulomas measuring a few millimeters (136). Organisms are found at the periphery of necrotic granulomas and within giant cells, easily identified in sections stained with hematoxylin and eosin. Multiple buds from a single cell, 10 to 60 m in diameter, are diagnostic, but less common. Rhizopus oryzae frequently invades blood vessels and disseminates through the blood. Morrison and Mcglave (146) reported mucormycosis in 13 of 1500 bone marrow transplant recipients (0. Involvement of the urinary tract may be clinically silent or show signs of renal infection, including flank pain, dysuria, gross hematuria, and acute renal failure (136). Renal involvement occurs in 50% of patients dying of disseminated mucormycosis (136). Microscopically, there is suppurative, necrotizing inflammation with thrombosis of interlobar and arcuate arteries. Granulomatous inflammation, fibrosis, and Langerhans-type multinucleated giant cells are seen. Organisms can be identified with Grocott methenamine silver stain or fluoresceinated antibodies (136). Viral Nephropathies Viral Pathogenesis and Tropism in the Kidney When encountering a host, eukaryotic cell viral pathogenesis requires an initiation phase in which the virus must first cross the cell membrane and enter the cell usually through a receptormediated process. Finally, during the release phase, assembly and maturation precedes the exit of the virus from the cell. Viruses have evolved several subversion mechanisms at all of these phases, which require the large-scale use of the host cellular machinery. Viruses can play a role in inducing cellular mechanisms of kidney injury and involve the kidney as an "innocent bystander" though a number of mechanisms (148). Heterologous immunity, in which established memory T-cell responses to a previously encountered pathogen, can have a major impact on the course and outcome of a subsequent infection with an unrelated pathogen. Heterologous immunity is dependent on the sequence of infections, the prior T memory network at the time of the infection, and can be either beneficial or detrimental to the host in transplantation settings (149).
While there is a mechanism to deal with the small amounts of light chains that circulate in normal individuals hiv infection rate in uganda buy monuvir 200 mg visa, that is not the case concerning heavy chains, because they cannot be filtered though the glomerulus owing to their high molecular weight. If free heavy chains are released to the circulation, they interact with the capillary endothelium and mesangium, where they engage in pathologic processes. Presumably, the physicochemical characteristics of the particular heavy chains will dictate how they produce pathology. The urine must be properly concentrated to detect small amounts of the monoclonal light chains. Immunoelectrophoresis or immunofixation may be necessary to confirm a diagnosis in some instances. Immunofixation electrophoresis, a faster technique than immunoelectrophoresis, is the most sensitive and commonly used method available for the detection of monoclonal proteins. It is very helpful in identifying a monoclonal protein associated with a polyclonal increase of light chains, subtle bands associated with faint monoclonal or biclonal proteins, and monoclonal heavy chain fragments in the urine. Clarification of banding patterns noted on electrophoresis gels is possible by direct comparison of results. The superior resolution, simplicity, and enhanced sensitivity of immunofixation make it the diagnostic modality of choice to detect monoclonal gammopathies. One caution with immunofixation is that it requires precise dilution of the antibodies to avoid a prozone effect (42). High-resolution electrophoresis (thin-layer agarose gels) may be combined with transfer onto nitrocellulose, followed by resolution of bands with monospecific enzyme-tagged antisera or monoclonal antibodies (Western blotting). This procedure is extremely sensitive, is more discriminating than immunofixation, and allows detection of minute amounts of monoclonal light chains (75). The technique can be utilized in selected instances when the monoclonal protein is in very small amounts. If there is an increase of polyclonal plasma cells or renal function impairment, both and light chains will increase, but the ratio of and light chains will remain normal. In contrast, a monoclonal increase of either or light chains by a neoplastic clone of plasma cells will alter the ratio, providing a numerical indicator of clonality. They are particularly useful in the diagnosis and monitoring of patients with light chain cast nephropathy (myeloma kidney) (76). The majority of the nephrotoxic light chains (approximately 70%) affect the tubulointerstitial compartment and are referred to as tubulopathic. The other 30% of nephrotoxic light chains preferentially involve the glomerular compartment, producing glomerulopathies (glomerulopathic light chains). The physicochemical characteristics of the involved immunoglobulin molecule appear to be a crucial pathologic determinant. There are also some uncharacterized host factors that may influence the pathologic alterations and the degree of damage. Genetic polymorphism represents an important consideration that has not been studied. Each of the diseases has specific clinical manifestations, pathologic findings, pathogenesis, prognosis, and management, and these specific features support viewing them as separate diseases. The glomerular and vascular compartments are not typically affected by the tubulopathic light chains. Amyloidosis and the deposition diseases generally exhibit glomerular manifestations, but they are also commonly associated with tubulointerstitial and vascular pathology. Infiltration of the renal parenchyma by neoplastic plasma cells is rare and usually occurs in terminal patients with myeloma (80). Renal insufficiency or failure because of renal parenchymal infiltration is very unusual.
|