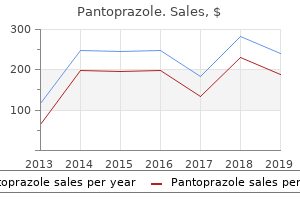
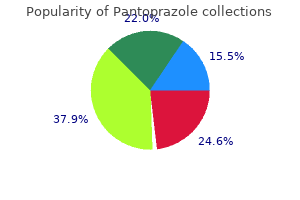
Pantoprazole"Best 40 mg pantoprazole, jenis diet gastritis". By: T. Rakus, M.B. B.CH. B.A.O., M.B.B.Ch., Ph.D. Co-Director, Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences F. Edward Hebert School of Medicine There appears to be little correlation between these histological patterns and the clinical course of the tumour but features such as increased cellular Classification the World Health Organization (1992) gastritis diet аукро pantoprazole 40mg with mastercard, related to the tissues of origin and histopathological features. The stroma of the epithelial tumour group is of a fibrous nature and does not contain any ectomesenchymal component. Subtypes of ameloblastomas are differentiated (intra-, extraosseous, desmoplastic, unicystic). A neoplastic and non-neoplastic line of the ameloblastic fibroma and ameloblastic fibrodentinoma is proposed. Ameloblastic carcinoma is differentiated from malignant (metastasizing) ameloblastoma. Also, the malignant epithelial odontogenic ghost cell tumour is termed calcifying ghost cell odontogenic carcinoma. Treatment (see also Chs 4 and 5) Ameloblastomas expand rather than destroy bone, but there is also some local invasion. The treatment of choice, therefore, is surgical excision of the tumour together with removal of a margin of normal bone but retention of the lower border of the mandible. Metastatic dissemination is rare and usually occurs by aspiration to the lungs following longstanding local disease or previous surgical intervention. Maxillary lesions are characterized by extensive involvement of the alveolar bone, antrum and zygomatic process. Clinically, the myxoma is an intrabony lesion that slowly expands the bony cortex and only perforates later. The lesion is rarely painful, but there may be loosening and displacement of the teeth. On microscopic examination of biopsy specimens, spindle/stellate shaped cells are present in an intercellular mucoid stroma, sometimes containing nests of epithelial cells. On radiographs, the tumour appears as a unilocular radiolucency sometimes with radio-opaque foci. A clinical provisional diagnosis should include either a lateral periodontal cyst or a dentigerous cyst, particularly as, in the latter case, the tumour is sometimes associated with an unerupted tooth. On histological examination, the tumour is encapsulated and consists of sheets and strands of epithelial cells arranged as convoluted bands and tubular structures. In the tubular structures, ameloblast-like cells are arranged radially around spaces containing a homogeneous eosinophilic material. The nature of this material is unknown, although suggestions have included pre-enamel, pre-dentine, amyloid and basement membrane material. Separate from the homogeneous material, foci of calcification frequently are evident throughout the lesion. The tumour contains little intervening mesenchymal stroma, although cystic degeneration of this tissue is common. Treatment (see also Chs 4 and 5) Myxomas infiltrate and, therefore, should be treated with surgical excision of the tumour and removal of a margin of normal bone. It has no gender predilection and is most frequent in the mandibular premolar-molar region. Radiographically, the tumour usually appears as a radiolucency containing focal opacities. Histological examination shows three distinct features: 294 intrabony swelling, which is occasionally painful. Clinically, the lesion presents as a gradually increasing Sheets of epithelial cells (containing tonofilaments, desmosomes and hemi-desmosomes), which are pleomorphic and contain abnormal nuclei. Concentric masses of calcified tissues: often closely associated with the epithelial cells. The tumour generally presents in close relation to the root of a tooth, the crown of an unerupted tooth, or in the site of a tooth that is congenitally missing. Histologically, the lesion consists of fibrous tissue which has a similar appearance to the dental pulp, but contains small nests of odontogenic epithelium. Either jaw of either sex may be affected, but most are anterior to the first molar. If there is any doubt about the advisability of bringing the patient to the department gastritis diet из purchase pantoprazole 40 mg without a prescription, consult a radiologist. Theatre radiography is done only when its results are needed during the operation. Alternatively, stimulate parotid salivary flow with 1 mL 10% citric acid on to tongue; flow rates < 1 mL/min may signify reduced salivary function. Plain radiography this is useful in the diagnosis of fractures, dislocations, bone and tooth disorders, joint disease and foreign bodies. Intra-oral radiography Chest radiography the chest radiograph is valuable in investigating chest disease, heart disease. Periapical radiographs are useful for demonstrating pathology in the periapical region (abscess, granuloma, cyst, etc. Bitewing radiographs show both upper and lower premolar and molar teeth on one film, but do not show the tooth apex. They are useful for revealing approximal caries and demonstrating the alveolar crest. Occlusal films may be useful in assessing the facial and lingual cortices and adjacent areas such as floor of mouth and palate. Abdominal radiography Abdominal radiographs are valuable in the diagnosis of gastrointestinal obstruction or perforation, renal stones or 30 gallstones. It involves injection of radioopaque contrast media (usually iohexol or iopamidol) in to the lower space of the temporomandibular joint. Angiography Angiography involves injection of radio-opaque contrast media in to arteries (arteriography) or veins (venography). Sialography is not commonly used nowadays but can occasionally help to: diagnosis or delineation of vascular anomalies or tumours assessment of tumours in the deep lobe of the parotid gland assisting surgical procedures. It has considerable advantages for visualizing complex head and neck anatomical 31 detect ductal obstruction detect the rare cases of salivary aplasia. Salivary scintigraphy Intravenous sodium pertechnetate is taken up by salivary (and thyroid) glands and secreted in saliva. Scintiscanning is not commonly used in salivary gland investigation but can sometimes help in the diagnosis of: Intra-oral areas inaccessible to conventional radiographs and is good for visualizing hard tissue lesions especially. T2, which depends on the gradual dephasing of the protons in the transverse or transaxial plane (spin-spin, or transverse relaxation times). When the sound strikes the interface between media, the energy reflects as an echo, which may be displayed as a unidimensional wave image (an A scan) or, when a sweeping beam is used, as a twodimensional monochrome image (a B scan). There is abrupt impedance with calcified lesions, or foreign bodies, such as glass or metal. Endoscopy Endoscopy is typically performed with flexible fibre-optic endoscopes, under local analgesia, sometimes with conscious sedation or general anaesthesia. However, cardiac pacemakers, insulin pumps, neurostimulators, cochlear implants, etc. Typically minor, such bleeding may simply cease spontaneously or be controlled by cautery. Perforation, however, generally requires surgery, though some cases may be treated with antibiotics and intravenous fluids. Photography this is exceedingly useful to record lesions, and the advent of digital photography has considerably improved the quality. Many allergies have a hereditary component but the prevalence of allergies appears to be increasing and people who suffer allergies to one type of substance are more likely to suffer allergies to others. Common allergens are pollen, dust mites, mould, pet dander, nuts, shellfish, milk and egg proteins and latex but, in many cases, the allergen cannot be reliably identified. Diagnosis is based on clinical history and presentation including a family history of allergy; plus skin-prick or patch testing to identify contact allergens (see above); or an elimina33 tion diet to identify food allergens. Haematinics may be lacking from dietary or gastrointestinal causes, or from increased losses. Dietary sources of iron and B12 are largely animal, while folate is present in green vegetables. 40 mg pantoprazole amex. TESCO HEALTHY FOOD SHOP.
It is probably a variant of atypical (idiopathic) facial pain chronic gastritis years cheap pantoprazole 20 mg otc, and should be managed similarly. Update on neurosurgical treatment of chronic trigeminal autonomic cephalalgias and atypical facial pain with deep brain stimulation of posterior hypothalamus: results and comments. Long-term follow-up of patients with atypical facial pain treated with amitriptyline. Clinical characteristics and diagnosis of atypical odontalgia: implications for dentists. Facial pain as first manifestation of lung cancer: a case of lung cancer-related cluster headache and a review of the literature. Prolonged gingival cold allodynia: a novel finding in patients withatypical odontalgia. Dental and periodontal therapies may be associated with a flare-up of oral ulcers in the short term, but may decrease their number in longer follow-up. In those countries it is a leading cause of blindness, though this is not often the case in the Western world. Circulating autoantibodies against a number of components, including intermediate filaments found in mucous membranes, cardiolipin and neutrophil cytoplasm, are present. There are raised levels of acute phase proteins and circulating immune complexes and changed levels of complement. There is immunoglobulin and complement deposition within and around blood vessel walls. Vasculitis: usually leukocytoclastic vasculitis underlies many of the clinical features (erythema nodosum, arthralgia, uveitis) as in established immune complex diseases/ vasculitis. Endothelial dysfunction in vasculitis may be detected by assay of a novel autoantigen Sip1 C-ter. The most common ocular manifestation is relapsing iridocyclitis, but uveitis with conjunctivitis (early) and hypopyon (late), retinal vasculitis (posterior uveitis), iridocyclitis and optic atrophy can arise. Skin lesions include erythema nodosum-like lesions, papulopustular lesions and acneiform nodules. Cardiac, or large vein thrombosis (of the inferior vena cava and cranial venous sinuses), can be life-threatening. Involvement of the joints, epididymis, heart, intestinal tract, vascular system and most other systems (though not in every case). This includes a history of repeated sore throats, tonsillitis, myalgias, and migratory arthralgias without overt arthritis but features can also include: *See text for details and glossary for abbreviations. The differential diagnosis is mainly from other oculomucocutaneous syndromes such as: recurrent genital ulceration eye lesions skin lesions Table 36. Thromboses of large veins, such as the dural sinuses or venae cavae Intestinal lesions: inflammatory bowel disease with discrete ulcerations Lung disease: pneumonitis Renal disease: haematuria and proteinuria Sweet syndrome: oral ulcers, conjunctivitis, episcleritis, inflamed tender skin papules or nodules Erythema multiforme: erosions, target (iris) lesions Pemphigoid: bullae, erosions Pemphigus: erosions, flaccid skin bullae Reiter syndrome: ulcers, conjunctivitis, keratoderma blenorrhagica Ulcerative colitis Syphilis Lupus erythematosus Mixed connective tissue disease. Mortality though low, but can result from neurological involvement, vascular thromboses, bowel perforation or cardiopulmonary disease, or as a complication of immunosup241 pressive therapy. The adverse effects of these agents may need to be accepted in such a serious condition (Ch. Thalidomide effectively controls ulcers with a dose of 25 mg daily, followed by a median maintenance dose of 100 mg/ week. Adverse events are reported by 85% but are mostly mild (78% of patients), sometimes severe (21%). Nevertheless, after 40 months of follow-up, 60% of patients in some studies were still receiving continuous or intermittent maintenance therapy with favourable efficacy/tolerance ratios. Mycophenolate mofetil is ineffective in the treatment of mucocutaneons Adamautiadtes- Behcets disease. The clinical application of etanercept in Chinese patients with rheumatic diseases. The stomas should be separated enough to allow the use of a stoma bag acute gastritis symptoms nhs purchase pantoprazole cheap, which covers only the functional stoma. It is the most valuable and accurate diagnostic study to define the anatomy of the anorectal malformation. Water-soluble contrast medium is instilled in to the distal stoma, which fills the distal intestine and enables demonstration of the location of the blind rectum and the precise site of a rectourinary fistula. The rectum is surrounded by striated muscle, which keeps it collapsed and prevents filling of the most distal part. To avoid this problem, the contrast medium must be injected with considerable hydrostatic pressure under fluoroscopic control. In this latter case, the surgeon can prepare the patient for an additional laparoscopy or laparotomy to mobilize a very high rectum. An electric stimulator is used to elicit muscle contraction during the operation as a guide to remain exactly in the midline. An incision that starts in the lower portion of the sacrum and extends anteriorly to the anal sphincter is necessary for rectoprostatic fistulas. Rectoperineal fistulas require a very small posterior sagittal incision (minimal posterior sagittal anoplasty). About 90 percent of male defects can be repaired via the posterior sagittal approach without entering the abdomen. The crossing of the muscle complex fibers with the parasagittal fibers represents the anterior and posterior limits of the new anus. In cases of rectourethral bulbar fistulas, the distal rectum is prominent and it almost bulges in to the wound. The rectum is opened between the sutures and the incision is continued distally, exactly in the midline, down to the fistula site. Multiple 6/0 silk sutures are placed through the rectal mucosa immediately above the fistula in a semi-circle. During this delicate dissection, it is very helpful to dissect the rectum laterally first, very close to the rectal wall and then anteriorly, until both dissections (lateral and medial) meet, separating the rectum completely from the urinary tract. The dissection must be performed between this fascia and the rectal wall to avoid damage to the innervation of the bladder and genitalia. In cases of a fistula opening in to the bulbar urethra, the dissection necessary to pull the rectum down to the perineum is minimal, whereas in cases of prostatic fistula the perirectal dissection is considerable. In both cases, enough rectal length must be gained in order to perform a comfortable, tension-free anastomosis between the rectum and the skin. The size of the rectum can be evaluated and compared with the available space so that its size matches the limits of the sphincter. The part of the intestine that will be adjacent to the closed rectourethral fistula must be normal rectal wall to avoid a recurrent fistula. The electrical stimulator is helpful in identifying the limits of these muscle structures. In cases in which the incision is extended anteriorly beyond the limits of the sphincter, it is necessary to repair the anterior perineum with interrupted, long-term, absorbable sutures to bring together both anterior limits of the external sphincter. These sutures should include part of the rectal wall in order to anchor it and help to avoid rectal prolapse. The peritoneum should be divided around the distal rectum to create a plane of dissection to be followed distally. At the point where the rectum becomes narrow, where it communicates with the bladderneck, it should be divided. The surgeon must be careful to avoid damage to the vas deferens, which run very close to the bowel (illustration d). Gaining adequate length, particularly with a high rectum, is challenging, and must be meticulous so as to avoid devascularizing the distal rectum. Ligation of the inferior mesenteric vessels as high as possible, very close to their origin near the aorta, would mobilize the rectum, but would probably compromise the blood supply of the rectum because the arcades that connect the middle colic vessels with the inferior mesenteric ones may have been interrupted at the time of the colostomy creation. Instead, the surgeon must ligate the most distal branches of the inferior mesenteric vessels close to the rectum. The rectum should be preserved and never discarded as it performs a vital reservoir function.
|