Super Levitra"Order cheap super levitra online, wellbutrin erectile dysfunction treatment". By: N. Thorald, M.B. B.CH. B.A.O., Ph.D. Assistant Professor, The University of Arizona College of Medicine Phoenix Severe comminution of the innominate bone can cause separation of the anterior column from the remainder of the pelvis impotence help cheap super levitra 80mg without prescription. In this fracture there is disruption of the iliopectineal and occasionally the anterior rim lines depending on where the fracture occurs. C, Axial image at the level of the obturator ring shows two fractures of the inferior pubic rami (arrows). D, the main difference between an elementary transverse fracture and a T-shaped fracture is involvement of the obturator ring. A, Radiograph shows disruption of the iliopectineal line (curved arrow) and displaced vertical fracture of the left iliac wing (arrows). A, Radiograph shows a complex left acetabular fracture with displacement and comminution (open box). C, Three-dimensional (3-D) image shows the degree of distraction and the relationship of the fracture fragments. Judet R, Judet J, Letournel E: Fractures of the acetabulum: classification and surgical approaches for open reduction, J Bone Joint Surg 46A:16151646, 1964. Letournel E: Acetabular fractures: classification and management, Clin Orthop 151:81106, 1980. A triangular fragment of iliac bone remains attached to the sacroiliac joint and is conspicuous when the more anterior acetabular fragments displace medially. In bothcolumn fractures the iliopectineal, ilioischial, and posterior rim lines usually are disrupted as is the obturator ring. There are two other associated fracture types involving the columns that are relatively uncommon. An anterior column and posterior hemitransverse fracture has two components, an anterior column fracture and a second transversely oriented fracture that arises from the column fracture and is directed posteriorly. In this fracture the iliopectineal, ilioischial, anterior rim, and posterior rim lines are all disrupted. A posterior column and posterior wall fracture is the least common type of associated fracture. In this fracture there is a posterior wall fracture fragment that is displaced because the femoral head typically dislocates posteriorly. In this fracture the ilioischial and posterior rim lines become disrupted, while the anterior landmarks remain intact. Yu Acute inflammatory and infectious soft tissue disorders are important conditions that affect nearly 2 million people in the United States every year. Inflammation versus infection of the skin, subcutaneous tissues, and muscles is often difficult to differentiate clinically, and early detection and accurate diagnosis have a significant impact on the immediate course of treatment and on the magnitude of any subsequent complication and morbidity. Although many of these conditions present with similar clinical symptoms, the recognition of key laboratory and constitutional findings can aid in the diagnosis of specific diseases and determine whether surgical intervention is required. In many situations, important differentiating characteristics on imaging enable diagnosis. The infection often begins with minor disruption of the skin that allows the invasion of microorganisms into the subcutaneous tissues. Typically patients present with fever, focal pain and swelling, erythema and warmth, and leukocytosis. Radiographically cellulitis manifests with soft tissue swelling causing induration of the subcutaneous fat. Ultrasonography is the preferred modality for identifying retained foreign bodies, particularly those of wooden composition. Enhancement occurs after administration of intravenous gadolinium, differentiating these findings from nonspecific soft tissue edema. A phlegmon is a purulent inflammatory process that may either spread or become walled off into an inflammatory mass, often occurring without a bacterial infection. B, Axial T2-weighted image shows striated areas of increased signal intensity and perifascial fluid accumulation (arrows). C, Fat-saturated T1-weighted axial image after intravenous administration of contrast shows diffuse enhancement of the infected dermal and subcutaneous soft tissues. Clinically, early necrotizing fasciitis mimics cellulitis with fever, pain, tenderness, swelling, and erythema. An important observation is severe pain at onset that is out of proportion to local findings. The radial forearm free flap is not a good option for reconstruction of the hard palate causes of erectile dysfunction in 20 year olds discount super levitra 80mg online. Imaging studies to determine the arterial anatomy of the extremity are not necessary before harvesting. In V wedge resection, an angle wider than 45 degrees will give better aesthetic results. Limiting the wedge resection to the limits of lip tissue will achieve better aesthetic results. The latissimus dorsi flap cannot be raised as a pedicled flap for head and neck reconstruction because the pedicle will not reach to most sites. Both latissimus dorsi and serratus anterior muscle flaps can be raised based on the thoracodorsal artery. The distal portion of the latissimus dorsi muscle has the best blood supply for designing the skin paddle. To reduce shoulder morbidity, the surgeon should preserve the lower portion of the serratus anterior muscle when harvesting the serratus flap. The length of a rotation flap should be approximately four times the width of the defect in face reconstruction. The loss of function of the muscle will cause a noticeable functional deficit in adduction of the thigh. Peripheral vascular disease in the superficial femoral artery is a contraindication to use of this flap. The blood supply to the gracilis enters the muscle at the junction of the upper two thirds and lower one third. Have the greatest tension perpendicular to the proximal border of the flap (the base). The risk of a pathological fracture can be significantly reduced with prophylactic plating. The harvested bone is usually thick enough to accept dental implants in oromandibular reconstruction. The defect after maxillectomy with orbital preservation without an inferior orbital wall defect C. The defect after maxillectomy with orbital preservation and loss of the inferior orbital wall D. Synkinesis can happen if all the branches of the facial nerve are reanastomosed to the main trunk. If a zonal approach to facial reconstruction is used, the upper branch is rehabilitated with nerve grafts. In salvage laryngectomy after definitive chemoradiation therapy failure, primary closure is the most successful method in limiting occurrence of fistulas. The anterolateral thigh flap is not a viable option for circumferential pharyngeal defects. If the skin of the neck has to be excised with the tumor, the pectoralis major myocutaneous flap with split-thickness skin grafts is a viable option. In salvage laryngectomy after chemoradiation therapy failure, free flaps or pectoralis major flaps are only recommended if there is not enough tissue for primary closure. Most defects after transoral resection of the base of the tongue or tonsil will require reconstruction with a flap. A palatal island flap can be used to reconstruct the soft palate in salvage situations. The radial forearm free flap is not a good option in reconstructing soft palate defects larger than 50%. Tonsil and lateral pharyngeal wall defects in salvage situations are better repaired with free tissue transfer. A lateral marginal mandibulectomy defect in a nonirradiated patient with more than 1 cm of thickness of remaining mandible C. A split-thickness skin graft can be safely applied to the skull without periosteal coverage. Full-thickness large defects of the mucosa and buccinator muscle are better treated with acellular collagen matrix (AlloDerm) or split-thickness skin grafts. Buccal mucosa defects should always be reconstructed with distant tissues to avoid trismus.
Cranial gunshot injury can be described based on the location of the bullet at the time of injury and degree of penetration of the cranial vault: superficial injuries erectile dysfunction kuala lumpur purchase cheap super levitra online, in which there is no intracranial penetration; penetrating injuries; and perforating injuries, in which the bullet has entered and exited the skull. Vascular injury in penetrating brain injury can be the result of contact forces of the projectile or the shearing force of a pulsating temporary cavity, which can result in partial or complete transection of an arterial wall. There has been brain swelling, indicated by loss of cortical sulci and blurring of the gray-white margin. Brain Death Brain death is the irreversible loss of function of the brain, including the brainstem. Current standards for making the diagnosis of brain death require identification of the suspected cause of coma, determination that the coma is irreversible, performance of a clinical examination, and interpretation of the appropriate neurodiagnostic and laboratory data. Because brain death is a clinical diagnosis, laboratory and radiologic tests are indicated only when confounding variables must be ruled out or confirmatory evidence of brain death must be obtained, when the findings on clinical examination are equivocal, or a full examination cannot be performed. The absence of cerebral blood flow is generally accepted as a sign of brain death, which can be demonstrated on radionuclide perfusion studies. Subsequently a radionuclide perfusion study was performed for confirmation of absent cerebral perfusion. Overall patient treatment can be optimized using the diagnostic and prognostic information derived from current imaging techniques. Collins, and Valeria Potigailo Evaluation of skull base fractures can be daunting because of the complex anatomy and the multiple traumatic injuries that can occur in the same traumatic incident. In addition, there are many normal fissures and foramina in the skull base that can mimic fractures, potentially resulting in falsepositive and false-negative diagnosis. The importance of detection of skull base fracture is to prevent complications and morbidity. Therefore, rather than merely focusing on fracture detection, a more clinically useful and practical approach for evaluation of skull base trauma is to consider the clinical importance of various types of fractures and their potential complications. Examples of various types of skull base fractures will be presented, with inclusion of normal structures that can mimic fractures and result in misdiagnosis. Emphasis will be placed on a practical classification of fractures and their potential complications. Images in axial, coronal, and sagittal planes are reconstructed from the volumetric data set. There is a moderately displaced comminuted fracture through the right frontal sinus involving both the anterior and posterior walls (arrows in A). The fracture extends posteriorly and medially along the right orbital roof into the ethmoid air cells (arrow in B) with involvement of the right fovea ethmoidalis and planum sphenoidale. The fracture plane extends in a comminuted fashion through the right lamina papyracea and laterally into the right greater sphenoid wing at the level of the lateral orbital wall (arrows in D). A tiny focus of pneumocephalus is seen along the right orbital roof (arrow in E), indicating violation of the skull base. Attention to subtle pneumocephalus is important for evaluation of skull base fracture because this may be the only clue to an occult fracture. The importance of evaluation of skull base fractures is to go beyond fracture detection and consider the potential complications associated with the fractures. Image-viewing software now allows image reformation in any arbitrary planes, which can be useful for complex or subtle fractures. Conner and Flis have reported that the use of high-resolution multiplanar reformats results in improved detection rate (99%) of skull base fractures, although many fractures detected only on the high-resolution multiplanar reformats may have little clinical significance. This is usually performed sometime after trauma when patients present with persistent rhinorrhea or otorrhea. Through a lumbar puncture, iodinated contrast material is infused into the thecal sac. The cribriform plate contains multiple perforations that transmit olfactory nerves from the nasal mucosa to the olfactory bulb. The planum sphenoidale and lesser wing of the sphenoid bone form the posterior part of the anterior skull base. Anterior skull base fractures are frequently associated with injury of the other maxillofacial structures, the paranasal sinuses and the orbits.
Blood culture is positive in almost 80% of all cases male erectile dysfunction pills buy 80mg super levitra with mastercard, especially in those who have not been given antibiotics before sampling. The treatment should be prompt and includes early surgical drainage of the collection, not just of the soft tissue collection, but also of the intramedullary abscess, as well as medical management of the sepsis with the help of appropriate dose and duration of antibiotic therapy. The role of surgery is to improve the local environment by removing infected devitalized bone and soft tissue, decompressing a large abscess cavity and allowing for antibiotics to reach the abscess cavity. It involves open surgical drainage and debridement of the collection, not just of the soft tissue and subperiosteal collection but also of the intramedullary collection. The bone marrow cavity should be thoroughly debrided and curetted and a thorough wash needs to be given using copious amounts of normal saline. In severe cases, antibiotic impregnated cement beads can be inserted in the cavity for local sustained and continued release of antibiotics. This is an important step and the exact location and size of the sequestrum has to be studied in detail preoperatively to ensure complete removal of the same. Initially, empiric broad-spectrum antibiotics may be started till culture is obtained. For community-acquired infections in children, ampicillin-cloxacillin or amoxicillinclavulanate are appropriate antibiotics. In very young children and neonates, vancomycin along with third-generation cephalosporins can cover both gram-positive and gram-negative organisms. Children with sickle cell anemia are more prone to Salmonella infections and hence ceftriaxone may be used as the drug of choice. This is then followed by appropriate oral antibiotic therapy for up to 6 weeks on a case-to-case basis. This results from bone necrosis from chronic inflammation and subsequent vascular compromise of the subperiosteal bone. It often results in sequestrum formation and is thus a constant source of infection with a resultant discharging sinus. Surgery consists of debridement, sequestrectomy and antibiotic-impregnated cement bead insertion. Acute osteomyelitis around the metaphyseal and physeal region can result in physeal arrest with a physeal bar formation, which can cause either limb length discrepancy or angular deformities. It is very difficult to treat and more often than not requires extensive reconstructive surgery. Etiology and medical management of acute suppurative bone and joint infections in pediatric patients. Increasing prevalence of Kingella kingae in osteoarticular infections in young children. Osteomyelitis in combination with acute septic arthritis is a serious condition and requires emergent attention especially in children to prevent complications and often disastrous sequelae. Acute hematogenous osteomyelitis is the most common type of osteomyelitis, which occurs due to the bacterial seeding of the metaphyseal region. The child presents with typical pseudoparalysis with a tender, swollen limb with fever. Magnetic resonance imaging is increasingly becoming a primary modality of diagnostic investigation especially in early cases. Surgical management involves drainage of the subperiosteal and intramedullary collection, curettage of the involved bone and cortical decompression in indicated cases. Intravenous antibiotics are initially necessary followed by a course of oral antibiotics in many cases. It is one of the true orthopedic emergencies and as such requires prompt attention including likely surgical intervention and targeted medical management. This commonly occurs in the hip and shoulder where the proximal epiphysis is intra-articular. The third mechanism which commonly occurs in clinical setting is the direct inoculation. Septic arthritis in childhood has a bimodal distribution-the first peak is during neonatal period and infancy and the second peak is between somewhere 48 years of age. Boys and girls are almost equally affected though with a slight male preponderance. Buy 80mg super levitra. 4 hour ERECTION? Here’s what to do! | Family Feud.
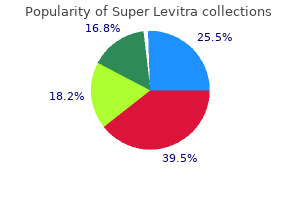
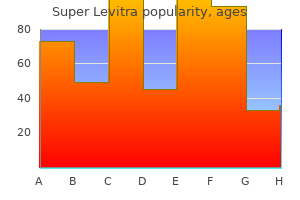
|