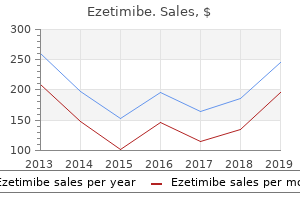
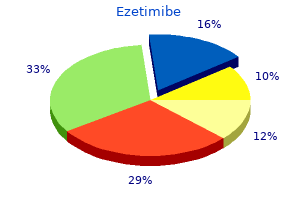
Ezetimibe"Buy ezetimibe australia, cholesterol levels check". By: F. Domenik, M.A., M.D. Co-Director, College of Osteopathic Medicine of the Pacific, Northwest Therefore cholesterol chart uk purchase ezetimibe 10mg with visa, nitrite tests should be performed on first morning specimens or specimens collected after urine has remained in the bladder for at least 4 hours. The reliability of the test depends on the presence of adequate amounts of nitrate in the urine. Further reduction of nitrite to nitrogen may occur when large numbers of bacteria are present, and this causes a false-negative reaction. The test is not designed to measure the concentration of leukocytes, and the manufacturers recommend that quantitation be done by microscopic examination. Neutrophils are the leukocytes most frequently associated with bacterial infections. Lymphocytes, erythrocytes, bacteria, and renal tissue cells do not contain esterases. Infections caused by Trichomonas, Chlamydia, yeast, and inflammation of renal tissues. Indoxylcarbonic acid ester Leukocyte Esterase Acid Specific Gravity the reagent strip test for specific gravity is included as part of the physical examination of urine in Chapter 4 and is reviewed here as part of the chemical examination. False-negative results may occur in the presence of high concentrations of protein (greater than 500 mg/dL), glucose (greater than 3 g/dL), oxalic acid, and ascorbic acid. This difference must be considered when comparing specific gravity results obtained by a different method. Leaving excess urine on the reagent strip after removing it from the specimen will: A. Failure to mix a specimen before inserting the reagent strip will primarily affect the: A. All of the following are important to protect the integrity of reagent strips except: A. All of the following will cause false-positive protein reagent strip values except: A. Testing for microalbuminuria is valuable for early detection of kidney disease and monitoring patients with: A. The primary chemical on the reagent strip in the MicralTest for microalbumin binds to: A. The principle of the protein-high pad on the Multistix Pro reagent strip is the: A. The principle of the creatinine reagent pad on microalbumin reagent strips is the: A. List the following products of hemoglobin degradation in the correct order by placing numbers 1 to 4 in the blank. A patient taken to the emergency department after an episode of syncope has a fasting blood glucose level of 450 mg/dL. If blood were drawn from this patient, how might the appearance of the serum be described What is the source of the substance causing the positive blood reaction and the name of the condition Considering the correct procedures for care, technique, and quality control for reagent strips, state a possible cause for each of the following scenarios. The urinalysis supervisor notices that an unusually large number of reagent strips are becoming discolored before the expiration date has been reached. The physician requests that the athlete collect another specimen in the morning prior to classes and practice. Is the proteinuria present in the first sample of prerenal, renal, or postrenal origin A construction worker is pinned under collapsed scaffolding for several hours prior to being taken to the emergency room. Its purpose is to detect and to identify insoluble materials present in the urine. The blood, kidney, lower genitourinary tract, and external contamination all contribute formed elements to the urine. Because some of these components are of no clinical significance and others are considered normal unless they are present in increased amounts, examination of the urinary sediment must include both identification and quantitation of the elements present. Microscopic analysis is subject to several procedural variations, including the methods by which the sediment is prepared, the volume of sediment actually examined, the methods and equipment used to obtain visualization, and the manner in which the results are reported. Protocols have been developed to increase the standardization and costeffectiveness of microscopic urinalysis, and they are discussed in this chapter. Populations that have come under consideration include pregnant women, as well as pediatric, geriatric, diabetic, immunocompromised, and renal patients. The midstream clean-catch specimen minimizes external contamination of the sediment.
Lyme arthritis Chapter 11 Synovial Fluid 227 Case Studies and Clinical Situations 1 cholesterol ranges for male order ezetimibe with a mastercard. A 50-year-old man presents in the emergency department with severe pain and swelling in the right knee. One membrane lines the cavity wall (parietal membrane), and the other covers the organs within the cavity (visceral membrane). The fluid between the membranes is called serous fluid, and it provides lubrication between the parietal and visceral membranes. Lubrication is necessary to prevent the friction between the two membranes that occurs as a result of movement of the enclosed organs, such as in the expansion and contraction of the lungs. Normally, only a small amount of serous fluid is present, because production and reabsorption take place at a constant rate. Production and reabsorption are subject to hydrostatic pressure and colloidal pressure (oncotic pressure) from the capillaries that serve the cavities and the capillary permeability. This action produces a continuous exchange of serous fluid and maintains the normal volume of fluid between the membranes. Abundant fluid (>100 mL) is usually collected; therefore, suitable specimens are available for each section of the laboratory. For better recovery of microorganisms and abnormal cells, concentration of large amounts of fluid is performed by centrifugation. Chapter 12 Serous Fluid serous fluids are frequently compared with plasma chemical concentrations because the fluids are essentially plasma ultrafiltrates. Effusions that form because of a systemic disorder that disrupts the balance in the regulation of fluid filtration and reabsorption-such as the changes in hydrostatic pressure created by congestive heart failure or the hypoproteinemia associated with the nephrotic syndrome-are called transudates. Classifying a serous fluid as a transudate or exudate can provide a valuable initial diagnostic step and aid in the course of further laboratory testing, because it is usually not necessary to test transudate fluids. Additional tests are available for specific fluids and will be discussed in the following sections. However, the significance of the test results and the need for specialized tests vary among fluids. Therefore, the interpretation of routine and special procedures will be discussed individually for each of the three serous fluids. Serous fluid cell counts can be performed manually by using a Neubauer counting chamber and the methods discussed in Chapter 9 or by electronic cell counters (see Appendix A). Any suspicious cells seen on the differential are referred to the cytology laboratory or the pathologist. In addition to the tests routinely performed to differentiate between transudates and exudates, two additional procedures are helpful when analyzing pleural fluid: the pleural fluid cholesterol and fluid:serum cholesterol ratio and the pleural fluid:serum total bilirubin ratio. A pleural fluid cholesterol >60 mg/dL or a pleural fluid:serum cholesterol ratio >0. If the blood is from a hemothorax, the fluid hematocrit is more than 50% of the whole blood hematocrit, because the effusion comes from the inpouring of blood from the injury. The appearance of a milky pleural fluid may be due to the presence of chylous material from thoracic duct leakage or to pseudochylous material produced in chronic inflammatory conditions. Chylous material contains a high concentration of triglycerides, whereas pseudochylous material has a higher concentration of cholesterol. Hematology Tests As mentioned previously, the differential cell count is the most diagnostically significant hematology test performed on serous fluids. The virus has not been shown to possess a transforming gene but may well activate a cellular oncogene cholesterol medication calculator trusted 10 mg ezetimibe. It is also possible that the virus does not play such a direct molecular role in oncogenicity, because the natural history of chronic hepatitis B infection involves cycles of damage or death of liver cells interspersed with periods of intense regenerative hyperplasia. This significantly increases the opportunity for spontaneous mutational changes that may activate cellular oncogenes. The incubation period may be as brief as 30 days or as long as 180 days (mean approximately 60-90 days). Acute hepatitis B is usually manifested by the gradual onset of fatigue, loss of appetite, nausea and pain, and fullness in the right upper abdominal quadrant. Early in the course of disease, pain and swelling of the joints and occasional frank arthritis may occur. With increasing involvement of the liver, there is increasing cholestasis, and hence clay-colored stools, darkening of the urine, and jaundice. In general, the symptoms associated with acute hepatitis B are more severe and more prolonged than those of hepatitis A; however, anicteric disease and asymptomatic infection occur. The infection-to-disease ratio, which varies according to patient age and method of acquisition, has been estimated to be approximately 3:1. One important difference between hepatitis A and hepatitis B is the development of chronic hepatitis, which occurs in approximately 10% of all patients with hepatitis B infection, with a much higher risk for newborns (~90%), children (~50%), and the immunocompromised. In immunocompetent adults, the strong cellular immune response results in acute hepatitis and only rarely (~1%) in chronic hepatitis. Sequence of appearance of viral antigens and antibodies in acute self-limiting cases of hepatitis B. Sequence of appearance of viral antigens and antibodies in chronic active hepatitis B. Treatment should be considered for patients with rapid deterioration of liver function, cirrhosis or complications such as ascites, hepatic encephalopathy, or hemorrhage as well as those who are immunosuppressed. For chronic hepatitis B diseases, pegylated or regular interferon- provides benefit in some patients. Safe sexual practices and avoidance of needlestick injuries or injection drug use are approaches to diminishing the risk of hepatitis B infection. Both active prophylaxis and passive prophylaxis against hepatitis B infection can be accomplished. Excellent protection has been shown in studies of men who have sex with men and in medical personnel. These groups and others, such as laboratory workers, injection drug users, travelers to endemic areas, persons at risk for sexually transmitted diseases, and those in contact with patients who have chronic hepatitis B, should receive hepatitis B vaccine as the preferred method of preexposure prophylaxis. Recently, immunization of newborns, all children, and adolescents has been recommended. Three intramuscular doses (at 0, 1, and 6 months) are given to achieve maximum titer. A combination of active and passive immunization is the most effective approach to prevent neonatal acquisition and chronic carriage in the neonate. A similar combination of passive and active immunization is used for unimmunized persons who have been exposed by needlestick or similar injuries. The procedure varies depending on the hepatitis B status of the "donor" case linked to the injury. Countries where 10% or more of persons with hepatitis B virus infection are also infected with hepatitis D virus (shown in black). Injection drug users are those at greatest risk in the western parts of the world, and up to 50% of such individuals may have IgG antibody to the delta virus antigen. Persons with chronic hepatitis B who acquire superimposed infection with hepatitis D suffer relapses of jaundice and have a high likelihood of developing chronic cirrhosis. Epidemics of delta infection have occurred in populations with a high incidence of chronic hepatitis B and have resulted in rapidly progressive liver disease, causing death in up to 20% of infected persons. The IgM antibodies appear within 3 weeks of infection and persist for several weeks, whereas IgG antibodies persist for years. Response to treatment in patients with delta hepatitis (and hepatitis B) is less than in those with hepatitis B alone. Persons infected with hepatitis B or D should not donate blood, organ, tissues, or semen. Safe sex should be practiced unless there is only a single sex partner who is already infected.
Because bacteria must synthesize folic acid rather than use it preformed from their environment cholesterol test error order generic ezetimibe from india, inhibition of those pathways is the basis of the antibacterial action of sulfonamides and trimethoprim. The biologic outcome of this inactivation depends on the function of the target protein. If it is a regulatory protein, the process it controls may be up- or downregulated. Two replication forks proceed in opposite directions until they meet at the replication termination site (ter). In fact, protein synthesis is the target of a greater variety of antimicrobials than any other metabolic process. All of these reactions involve activated building blocks that are polymerized or assembled within or on the exterior surface of the cytoplasmic membrane. The most unique of these is the peptidoglycan, which is completely absent from eukaryotic cells. The pentapeptide contains L-lysine in Staphylococcus aureus and diaminopimelic acid in Escherichia coli. The transpeptidation reactions in the formation of the peptidoglycan of Eshcerichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus are shown. These transpeptidases are involved in forging, breaking, and reforging the peptide cross-links between glycan chains necessary to permit expansion of the peptidoglycan sac during cellular growth. Moreover, many proteins are translocated through all layers of the cell envelope to the exterior environment. The latter instance is of particular medical interest when the protein is an exotoxin or other protein involved in virulence. Protein secretion has become the general term to designate all these instances of translocation of proteins out of the cytosol (ie, whether the protein is to leave the cell or become part of the envelope). The process is relatively simple in Gram-positive bacteria in which proteins, after export across the cytoplasmic membrane, have only to move through the relatively porous peptidoglycan layer. In Gram-negative bacteria, the periplasmic space and the outer membrane must also be traversed. These nanosyringe injection systems are a major mechanism for the delivery of exotoxins and other proteins important in the pathogenesis of human infections. The amino-terminal end of the preprotein has a signal peptide that facilitates transport through the apparatus by chaperone (SecB) and proteins that form channels (SecY, SecE, SecG) or have propelling functions (SecA). Proteins are transported across both membranes and then injected by a syringe apparatus. A recently discovered sixth type of secretion system resembles the cell-puncturing devices of bacteriophages and thus can inject into bacteria as well as eukaryotic cells. Using methods described in Chapter 4, growth of a liquid bacterial culture can be monitored by counting colonies from samples removed at timed intervals or by turbidity measured in a spectrophotometer. The growth rate of a bacterial culture depends on three factors: the species of bacterium, the chemical composition of the medium, and the temperature. The time needed for a culture to double its mass or cell number is in the range of 30-60 min for most pathogenic bacteria in rich media. Some species can double in 20 minutes (E coli and related organisms), and some (eg, some mycobacteria) take almost as long as mammalian cells-20 hours. When first inoculated, liquid cultures of bacteria characteristically exhibit a lag period during which growth is not detectable. During this lag phase, the cells are actually quite active in adjusting the levels of vital cellular constituents necessary for growth in the new medium.
Host cells normally produce a protein that inhibits expression of papillomavirus transforming genes cholesterol eggs or bacon purchase ezetimibe 10 mg free shipping, but this can be inactivated by products of the virus and possibly by other infecting viruses, thus allowing malignant transformation to occur. E6 accelerates the degradation of p53, a tumor suppressor protein, and reduces its stability. Respiratory papillomatosis due most often to types 6 and 11 occurs as intraoral or laryngeal lesions. They are often found on the head or shaft of the penis, at the vaginal opening, or perianal 4 to 6 weeks after exposure. Lesions may increase in size to cauliflower-like appearance during pregnancy or immunosuppression. Colposcopic photograph of cervical transformation zone with diffusely scattered acetowhite staining, characteristic of hpV infection. Most abnormal smears in young women are due to human papillomavirus (hpV) infection; when persistent, it is considered an important factor in the development of cancer of the cervix. Papillomavirus infection leads to perinuclear cytoplasmic vacuolization and nuclear enlargement, referred to as poikilocytosis, in epithelial cells of the cervix or vagina. Among the topical cytotoxins are podophyllin, podophyllotoxin, 5-fluorouracil, and trichloroacetic acid. Another procedure called conization, also known as cone biopsy, removes abnormal cells. Cervical and anal lesions may be treated with electrocautery, but carcinoma may require radiation therapy or radical surgery. The vaccine can be administered to girls aged 9 to 12 years and to adolescent girls and women aged 13 to 26 years who have not completed or started the vaccine. Gardasil can be given to adolescent boys and men aged 13 to 26 years to prevent genital warts. Cervarix and Gardasil are given intramuscularly as a three-dose series over a 6-month period. However, these viruses are able to transform cells of a variety of heterologous cell lines in culture. However, respiratory or oral transmission (due to contaminated food or water) is suspected. However, the viruses remain latent and may reactivate and cause disease in immunocompromised patients. The reason polyomaviruses fail to produce tumors in their natural hosts is uncertain, but it may be because these viruses are usually cytocidal under these conditions. From a biologic point of view, the polyomaviruses are particularly useful models of oncogenicity because they can be readily studied in vitro and interact with cells in different ways. In some, they produce lytic infections and cell death with the production of complete virions. In others, they integrate randomly into the cell genome and cause transformation by the expression of one or more of the viral genes. The disease is characterized by the development of impaired memory, confusion, and disorientation, followed by a multiplicity of neurologic symptoms and signs that include hemiparesis, visual disturbances, incoordination, seizures, and visual abnormalities. Pathologically, foci of demyelination are found, surrounded by giant, bizarre astrocytes containing intranuclear inclusions. The demyelination is due to viral damage to oligodendroglial cells, which synthesize and maintain myelin. Treatment consists of reducing immunosuppression, but up to 50% of the patients with this syndrome may require nephrectomy. The molecular mechanisms of persistent viral infections are not clearly understood, but three broad conditions must be satisfied for a virus to establish a persistent infection in a host: 1. Viruses have found various cell types such as nonpermissive cells in a host to infect and remain less cytolytic to maintain persistence. Order ezetimibe 10mg on line. Are Eggs Bad? Do They Cause High Cholesterol or Herpes? The TRUTH.
|