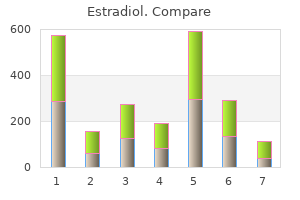
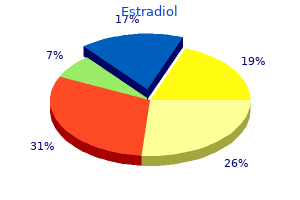
Estradiol"1 mg estradiol with amex, menstruation late". By: F. Emet, M.B.A., M.B.B.S., M.H.S. Associate Professor, Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine They are commonly observed in response to therapy in deficiency anemias and hemolytic anemia recent women's health issues buy estradiol 2mg low price. These may be seen in patients with infections, burns, trauma, pregnancy or cancer. It results from conversion of citrate (present in stored blood) and lactate (accumulated due to hypoperfusion) to bicarbonate 292 Anemia and Red Blood Cells 132. Still the risk of severe hemolytic reactions is much more with single donor incompatible platelets than pooled plasma because the dose of incompatible plasma is also increased. As Rh negative blood is often in limited supply, Rh positive blood is used in the emergency transfusion of older females and males of unknown blood group. In such cases sensitization may occur but the risk of an immediate hemolytic reaction is low. O blood group is the universal donor and therefore, should be given to this patient. So, the preferred answer is post splenectomyQ 293 Review of Pathology Howell-Jolly bodies are nuclear remnants seen in red cells, intermediate or late normoblasts. It is inherited as an X-linked recessive traitQ and thus affects mainly males and homozygous females. Accordingly, serum erythropoietin levels in polycythemia vera are very low, whereas almost all other forms of absolute polycythemia are caused by elevated erythropoietin levels. In this sdiorder, there is an increase in the activated partial thrombolastin time and normal values of prothrombin time. As gestational age increases, the chains are replaced by the chains, resulting in formation of adult hemoglobin, HbA. HbA1c is glycated hemoglobin and is used for both diagnosis and checking the compliance of a patient having diabetes mellitus. These cells have a very high turnover rate, so the macrophages that happen to be hanging around get stuffed with cellular debris (they are at this point called "tingible body macrophages"), and upon fixation, the cytoplasm falls away, leaving round white spaces filled with debris (the "stars"). Therefore, infants rapidly develop antibodies against the antigens not present in their own cells. This H substance is formed by the addition of fucose to the glycolipid or glycoprotein backbone. The subsequent addition of N-acetylgalactosamine creates the A antigen, while the addition of galactose produces the B antigen. Page 665 Blood products are often responsible for saving lives of individuals but may be associated with the development of the complications. Allergic Reactions: Severe, potentially fatal allergic reactions may occur when blood products containing certain antigens are given to previously sensitized recipients. Urticarial allergic reactions may be triggered by the presence an allergen in the donated blood product that is recognized by IgE antibodies in the recipient. Hemolytic Reactions: Acute hemolytic reactions are usually caused by preformed IgM antibodies against donor red cells that fix complement. Clinical features include fever with chills, flank pain, intravascular hemolysis, and hemoglobinuria. Lesions include erythema nodosum, subcutaneous nodules, erythematous plaques and lupus pernioQ menstruation yoga practice buy cheap estradiol 1 mg. Unilateral or bilateral ocular involvement resulting in iritis, glaucoma or corneal opacity may occur. Causes lacrimal gland inflammation (causing dry eyesQ) and salivary gland involvement (dry mouthQ). These patients also demonstrate skin anergy and a restrictive pattern on pulmonary functiontests. Clinical features include Progressively increasing dyspnea (difficulty in breathing), tachypnea resulting in respiratory failure, cyanosis and hypoxemia, chest x-ray shows bilateral diffuse infiltration ("white out" lungQ). Prevention of hyaline membrane disease is by delaying the onset of labor and administra tion of glucocorticoids to the mother. Steroids increase the formation of surfactant lipids and proteins thereby decreasing the respiratory distress. Pulmonary Hypertension It is defined as increased pulmonary artery pressure, usually due to increased vascular resistanceorbloodflow. Increased hydrostatic pressure as in left-sided heart failure, mitral valve stenosis, fluidoverload,etc. The lungs are wet and heavy and the fluid accumulation is more in the lower lobes. Bronchogenic Cancer Metastasis/Secondaries are the commonest malignant tumor of the lung. However,bronchogenic cancer is the most common primary malignant tumor of the lung. Due to involvement of the airways, the patient usually dies by suffocation (not by metastatic spreadQ). Clinical features: Cough is the most common symptom in these patients which is followed by weight loss and dyspnea. Horner syndrome Horner syndromeQ is caused due to compression of sympathetic nerve plexus by an apical tumor called as Pancoast tumorQ. Hypertrophic pulmonary osteoarthropathy having clubbing and periosteal new bornformation. This is the gold standard of diagnosis Malignant Mesothelioma is not associated with smoking. Concept Respiratory System the best marker to differentiate benign and malignant mesothe lioma is p53. Its mutation is present in malignant meso thelioma and this mutation is absent in benign mesothelioma. A 9 year old girl Bandhini developed a 10 mm area of induration on the left forearm 72 hours after intradermal injection of 0. On the third post operative day, he complains of increasing difficulty in respiration. The finger probe reveals presence of pO2 of 60 mm Hg but the patient is afebrile to touch. One evening the resident doctor notices that Mr Thapa coughs up copious mucoid sputum following which his condition improves dramatically. In a heavy smoker with chronic bronchiolitis, which of the following is likely to be seen: (Kolkata 2003) (a) Centrilobularemphysema (b) Panacinaremphysema (c) Paraseptalemphysema (d) Noneoftheabove 22. A 37 year old male Ranjir Kapoor presents to the hospital with progressive exertional dyspnea. His symptoms began insidiously but have progressed gradually to the extent that now he has a problem even in his daily activities. A 30 year old woman Chinamma has had increasing dyspnea with cough for the past week. On examination, she is afebrile but has extensive dullness to percussion over all the lung fields. Autopsy of a person reveals a small cluster of caseating granulomas in the right lung just above the interlobar fissure and similar granulomas in the hilar lymph nodes. Buy discount estradiol 1mg line. New Govt Scheme for Pregnant women in Telugu States.
The aim of this chapter is to summarize B-cell development in primary and secondary lymphoid tissues women's health menstrual issues purchase estradiol 2 mg on-line. The final sections of the chapter outline B-cell maturation in secondary lymphoid tissues. The information presented provides a basis for understanding abnormalities of B-cell development, such as leukemia, lymphoma, and immunodeficiency states that are discussed in other chapters. Studies in mice have contributed much to what is known about B-cell development and have served as a basis for understanding human B lymphopoiesis. Thus, although we emphasize the human literature as much as possible, frequent reference to findings in mice are made. Finally, after light chain gene rearrangements have occurred and light chain protein is expressed, pre-B cells mature into B lymphocytes that express the assembled Ig molecule on their surface. The phenotypic subdivision of cells within the pro-, pre- and B-cell compartments based on the differential expression of cell surface antigens is possible as shown in. Finally, productive rearrangement and expression of an Ig light chain gene result in maturation of pre-B cells into surface IgM expressing B-cells. These observations, combined with the analysis of genetically engineered strains of mice in which the genes encoding specific transcription factors have been deleted, have made it possible to obtain a sophisticated understanding of the transcriptional regulation of B-cell development. The developmental potential of hematopoietic cells is specified toward a lymphoid fate by products of the Ikaros gene. Ikaros is an interesting transcription factor because rather than activating gene expression, it acts as a repressor by associating with transcriptionally silent genes in foci containing heterochromatin. Advances in the development of monoclonal antibodies to leukocyte cell surface antigens and in flow cytometry have made it possible to isolate murine and human B lineage progenitors at various stages of development. Stages of human and murine B-cell development and selected cell surface, cytoplasmic, and nuclear determinants expressed at various stages of differentiation are shown. However, if the gene encoding Pax5 is introduced into Pax5-deficient precursors, this developmental promiscuity is no longer observed. Pax5 also may inhibit the T-cell potential of lymphoid-restricted progenitors by antagonizing expression of Notch1, a cell-surface receptor whose stimulation activates signaling pathways required for commitment to the T-cell lineage. In addition to regulating commitment to the B-cell lineage, continued Pax5 expression is necessary to maintain lineage fidelity even in relatively mature B cells. The heavy chain gene consists of distinct variable (V), diversity (D), joining (J), and constant (C) regions. The V region genes are located at the 5 end of the Ig heavy chain locus, and each consists of approximately 300 base pairs. These genes, which are separated by short intron sequences, are organized into seven families based on sequence homology. Finally, 10 C region genes representing alternative Ig isotypes are arranged in tandem. The first occurs at the pro-B to pre-B-cell transition and is dependent on successful recombination of the Ig heavy chain gene and expression of Ig heavy chain protein. The figure shows the Ig heavy chain gene and the signal sequences 3 of each V region locus, 5 and 3 of each D region locus, and 5 of each J region locus. These consist of heptamer and nonamer sequences separated by either 12 or 23 base pairs. During immunoglobulin (Ig) recombination, a signal sequence of 12 base pairs can only join to another of 23 base pairs (the so-called 12-23 rule). As shown in the figure, initial heavy chain gene rearrangements form coding joints between D and J regions as well as signal joints that are ultimately degraded. Sterile Transcripts Ig heavy chain gene rearrangement is preceded by transcription of the unrearranged heavy chain locus. This results in the production of developmentally regulated transcripts of unrearranged Ig genes, referred to as germline or sterile transcripts. Multiple species of sterile transcripts have been described, and some could conceivably encode proteins. A mechanistic link between transcription and Ig gene rearrangement has been hypothesized. Chapter 18 B-Cell Development 185 Immunoglobulin Heavy Chain Gene Rearrangement and Expression Subsequent to the appearance of sterile transcripts, Ig heavy chain gene rearrangements occur.
Aplastic anemia this is a disorder characterized by marrow failure associated with pancytopenia (anemia, thrombocytopenia and leukopenia) breast cancer history proven 1mg estradiol. The bone marrow biopsy shows it is characteristically hypocellular being replaced by fat cells (in contrast to aleukemic leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome in which we have pancytopenia associated with hypercellular marrow) whereas bone marrow aspiration reveals "dry tap". It is treated with either bone marrow transplantation (in young patients) or antithymocyte globulin (in old patients). Anemia of renal failure It is characterized by inadequate release of erythropoetin resulting in development of anemia. Haptoglobin followed by hemopexin form the defense against free heme in the plasma. At head region, spectrin binds to ion transporter, band 3 of membrane with the help of ankyrin and band 4. Mostly the mutations are seen in head region most commonly in ankyrinQ [Robbins 8th/e pg 642] and the next common mutation is in band 3 (Anion channel). This can occur due to ingestion of certain drugs or foods (consumption of fava beans), or more commonly, exposure to oxidant free radicals generated by leukocytes in the course of infections. Less severe membrane damage results in decreased red cell deformability leading to formation of spherocytes or removal of membrane by the macrophages leading to the presence of "bite cells". Both bite cells and spherocytes are trapped in splenic circulation resulting in their removal by erythrophagocytosis. Features of chronic hemolytic anemias like splenomegaly and cholelithiasis are absent because the hemolytic episodes occur intermittently. Since only older red cells are at risk for lysis, the episode is self-limited, as hemolysis stops when only Anemia and Red Blood Cells the younger red cells remain. The features of chronic hemolytic anemias like splenomegaly and cholelithiasis are absent because the hemolytic episodes occur intermittently. It is a potent inhibitor of C3 convertase, and thereby prevents spontaneous activation of the alternative complement pathway in vivo. These defects are not limited to red blood cells, as deficient platelets and granulocytes are also more sensitive to lysis by complement. The complement system is activated by acidotic conditions like exercise (accumulation of lactic acid) or sleep (due to decreased respiratory rate). Since the respiration decreases at night, so, patient experiences intermittent attacks (paroxysmal) of hemolysis at night (nocturnal) resulting in passage of red urine (hemoglobinuria) in the morning. In addition IgM can activate complement resulting in the cells being coated with C3b followed by extravascular hemolysis. The antibody is called the Donath-Landsteiner antibody (previously associated with syphilis, but also with mycoplasma pneumonia measles, mumps, and ill defined viral and "flu" syndromesQ. The endothelial layer of small vessels is damaged with resulting fibrin deposition and platelet aggregation. As red blood cells travel through these damaged vessels, they are fragmented resulting in intravascular hemolysis. It is identified by the finding of anemia and schistocytes, "burr cells," "helmet cells," and "triangle cells"on microscopy (should be > 3/5000 cells) and these should have 1-3 sharp spicules. Cold agglutinins: Are associated with Mycoplasma pneumonitits and infectious mononucleosis.
|