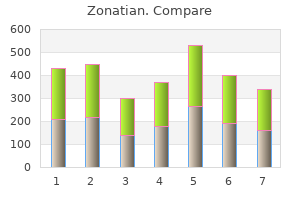
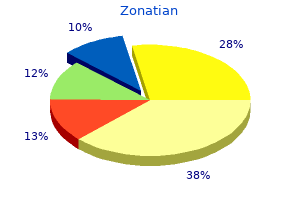
Zonatian"Discount zonatian 20 mg mastercard, skin care 30s". By: H. Ramon, MD Clinical Director, University of California, San Diego School of Medicine Radical mastectomy terribly disfigured and disabled countless women acne 2 weeks before period purchase 30 mg zonatian with visa, yet proved no more effective than simple mastectomy or lumpectomy. Surgery is generally followed by radiation or chemotherapy, and estrogen-sensitive tumors may also be treated with an estrogen blocker such as tamoxifen. A natural-looking breast can often be reconstructed from skin, fat, and muscle from other parts of the body. How do the site of female gamete production and mode of release from the gonad differ from those in the male List the subcutaneous erectile tissues and glands of the female perineum and state the function of each. Yet, a 1997 study of more than 17,000 girls in the United States showed 3% of black girls and 1% of white girls beginning puberty by age 3, and 27% and 7%, respectively, by age 7. The youngest mother known to history was Lina Medina of Peru, who began menstruating at 8 months of age, was impregnated at age 4, and gave birth at age 5, in 1939. Puberty is triggered by the same hypothalamic and pituitary hormones in girls as in boys (see section 27. A girl must attain about 17% body fat before she can begin to ovulate and menstruate, and adult women commonly cease if they drop below 22% fat. Leptin, the hormone secreted by fat cells, acts as an adiposity signal to the brain. Puberty is therefore delayed in undernourished girls, unusually thin girls, and in other girls with low body fat due to such vigorous and habitual physical activity as gymnastics and ballet. These hormone levels rise gradually from ages 8 to 12 and then more sharply in the early teens. Estrogen, progesterone, and prolactin initially induce the formation of lobules and ducts in the breast. Duct development is completed under the influence of glucocorticoids and growth hormone, while adipose and fibrous tissue enlarge the breast. Breast development is complete around age 20, but they undergo minor changes in each menstrual cycle and major changes in pregnancy. This probably reflects the fact, detailed later in this chapter, that it takes about 290 days for ovarian follicles to mature and ovulate. It stimulates growth hormone secretion and causes a rapid increase in height and widening of the pelvis. Estradiol is largely responsible for the feminine physique because it stimulates fat deposition in the mons pubis, labia majora, hips, thighs, buttocks, and breasts. Progesterone29 acts primarily on the uterus, preparing it for possible pregnancy in the second half of each menstrual cycle and playing roles in pregnancy discussed later. The sexes differ less in the identity of the hormones present than in their relative amounts-high androgen levels and low estrogen levels in males and the opposite in females. Another difference is that these hormones are secreted more or less continually and simultaneously in males, whereas in females, secretion is distinctly cyclic and the hormones are secreted in sequence. This will be very apparent as you read about the ovarian and menstrual cycles later in this chapter. Hot flashes may occur several times a day, sometimes accompanied by headaches resulting from the sudden vasodilation of arteries in the head. Menopause is the cessation of menstrual cycles, usually occurring between the ages of 45 and 55. It is difficult to precisely establish the time of menopause because the menstrual periods can stop for several months and then begin again. Menopause is generally considered to have occurred when there has been no menstruation for a year or more. Describe the major changes that occur in female climacteric and the principal cause of these changes. In women, it is accompanied by menopause, the cessation of menstruation (see Deeper Insight 28. Effects of pregnancy on blood volume and cardiac output; how pregnancy can cause edema skin care equipment purchase 20 mg zonatian, hemorrhoids, and varicose veins 8. Effects of pregnancy on respiratory function; the mechanism for enhancing diffusion of carbon dioxide from the fetal blood into the maternal blood of the placenta 28. The neuroendocrine reflex stimulated by the suckling of an infant, and the roles of oxytocin and prolactin in breast-feeding 5. How breast milk varies in composition from one time to another; which components of the milk are released early, and which are released nearer the end, of a single feeding 7. The daily quantity of breast milk typically produced (eventually) and its nutritional demands on the mother 9. Effects of pregnancy on glomerular filtration, urine output, and the capacity of the bladder 10. Effects of pregnancy on the skin; causes of striae (stretch marks), the linea nigra, and chloasma 11. The vertex position and the developmental age at which the fetus typically assumes it 12. The nature and possible cause of Braxton Hicks contractions, when they occur, and how they differ from true labor contractions 13. Factors that stimulate the onset of labor contractions; the roles of oxytocin, positive feedback, and the voluntary abdominal muscles in labor 28. Influences of estrogen, growth hormone, insulin, glucocorticoids, and prolactin on mammary gland development during pregnancy 2. The fluid secreted by the mammary glands for the first few days postpartum, how it differs from breast milk, and its benefits to the neonate Testing Your Recall 1. Of the following organs, the one(s) most comparable to the penis in structure is/are a. The hormone that most directly influences the secretory phase of the menstrual cycle is a. Smooth muscle cells of the myometrium and myoepithelial cells of the mammary glands are the target cells for a. A yellowish structure called the secretes progesterone during the secretory phase of the menstrual cycle. A tertiary follicle differs from a primary follicle in having a cavity called the. All the products of fertilization, including the embryo or fetus, the placenta, and the embryonic membranes, are collectively called the. The funnel-like distal end of the uterine tube is called the and has feathery processes called. A slim girl who is active in dance and gymnastics is likely to begin menstruating at a younger age than an overweight inactive girl. Women do not lactate while they are pregnant because prolactin is not secreted until after birth. Colostrum contains more fat than mature milk, ensuring the neonate of adequate Answers in Appendix A caloric intake in its first month of separation from placental nutrition. Would you expect puberty to create a state of positive or negative nitrogen balance Aspirin and ibuprofen can inhibit the onset of labor and are sometimes used to prevent premature birth. Review your knowledge of these drugs and the mechanism of labor, and explain this effect. At 6 months postpartum, a nursing mother is in an automobile accident that fractures her skull and severs the hypophysial portal vessels. If the ovaries are removed in the first 6 weeks of pregnancy, the embryo will be aborted. If they are removed later in pregnancy, the pregnancy can go to a normal full term. Explain the physiological link between hearing that sound and the ejection of milk. Discount zonatian 5mg overnight delivery. Men's Grooming Care Products To Use Every Day (Skincare & Sensitive Skin).
Centrioles Mid- to late prophase I Homologous chromosomes form pairs called tetrads acne marks buy generic zonatian 30 mg. Crossing-over Spindle fibers Metaphase I Tetrads align on equatorial plane of cell with centromeres attached to spindle fibers. Anaphase I Homologous chromosomes separate and migrate to opposite poles of the cell. Telophase I New nuclear envelopes form around chromosomes; cell undergoes cytoplasmic division (cytokinesis). Although we pass the same genes to our offspring as we inherit from our parents, we do not pass on the same chromosomes. This creates new combinations of genes and thus contributes to genetic variety in the offspring. After crossing-over, the chromosomes line up at the midline of the cell in metaphase I, they separate at anaphase I, and the cell divides in two at telophase I. Therefore, at the conclusion of meiosis I, each chromosome is still double-stranded, but each daughter cell has only 23 chromosomes- it has become haploid. Fertilization combines 23 chromosomes from the father with 23 chromosomes from the mother and reestablishes the diploid number of 46 in the zygote. The first stem cells specifically destined to become sperm are primordial germ cells. Like the first blood cells, these form in the yolk sac, a membrane associated with the developing embryo. In the fifth to sixth week of development, they crawl into the embryo itself and colonize the gonadal ridges. At puberty, testosterone secretion rises, reactivates the spermatogonia, and brings on spermatogenesis. The essential steps of spermatogenesis are as follows, numbered to match figure 27. One daughter cell from each division remains near the tubule wall as a stem cell called a type A spermatogonium. Type A spermatogonia serve as a lifetime supply of stem cells, so men normally remain fertile even in old age. The other daughter cell, called a type B spermatogonium, migrates slightly away from the wall on its way to producing sperm. The daughter cells from secondary spermatocytes through spermatids remain connected by slender cytoplasmic processes until spermiogenesis is complete and individual spermatozoa are released. Ahead of the primary spermatocyte, the tight junction between two nurse cells is dismantled, opening a door for the movement of the spermatocyte toward the lumen. Behind it, a new tight junction forms like a door closing between the spermatocyte and the blood supply in the periphery of the tubule. Now safely isolated from blood-borne antibodies, the primary spermatocyte undergoes meiosis I, which gives rise to two equal-size, haploid, and genetically unique secondary spermatocytes. A spermatid divides no further, but undergoes a transformation called spermiogenesis, in which it differentiates into a single spermatozoon (fig. The spermatid sprouts a tail (flagellum) and discards most of its cytoplasm, making the sperm a lightweight, self-propelled cell. Throughout their meiotic divisions, the daughter cells never completely separate, but remain connected to each other by cytoplasmic bridges. Eventually, however, the mature sperm separate from each other, depart from their supportive nurse cells, and are washed down the tubule by a slow flow of fluid. Spermatogenesis occurs in cycles, progressing down the tubule in spermatogenic waves. At any particular time, therefore, cells in a given portion of the tubule are at about the same stage of spermatogenesis, not evenly distributed among all stages.
A subsequent search of the scene found multiple rocks in the water below the bridge which suggested that in fact the individual had Water-going vehicles Water-going vehicles can attract a similar variety of asphyxia deaths to road-going vehicles acne treatment reviews purchase 20mg zonatian otc. One more specialized example that can pose a risk to the investigating team is 7 Crime Scene Investigation died during autoerotic water-based suspension practice which they had undertaken at this site on a number of previous occasions [14]. The cases involve more young males than females and often result from compression of the neck following the failure of a release mechanism. The presence of erotic material or professional or handmade implements at the scene may help with determining the circumstances behind the death. Many different everyday items can be used in autoerotic practice and there should therefore be careful consideration of everything at the scene. The authors have encountered the use of a modified vacuum cleaner to aid masturbation and are aware of a case involving a balloon fetish. Electrical stimulation may be part of the process, and this may pose an additional hazard at the scene. Comparative study of photogrammetric methods using panoramic photography in a forensic context. Where a pathologist does not attend the scene, it is important that they are fully briefed regarding the findings at the scene and have access to the scene photographs and/or video footage prior to the autopsy. Hydrogen protons exist mainly in water in the body, but also in fat, proteins and all soft tissues to some extent. Background Medical imaging techniques have been used in forensic investigations for over 100 years. Ultrasound imaging is a crucial tool in clinical examination of the neck, but it is less useful forensically so this will not be discussed. This attenuation is mainly due to tissue density, although atomic number also plays a part. Therefore bones, containing calcium, appear comparatively denser than soft tissues, even if they have similar density, and metals, unless of relatively low atomic number, can cause severe disruption of the image. The appearance of the image can be altered by how the image is created from the original data returned from the X-ray detectors. Basically, this reconstruction balances spatial resolution (edge enhancement) with contrast resolution (lesion detection). High spatial resolution (hard) algorithms are superior where there is already high contrast (bone- soft tissue or air-tissue interfaces) and reduce the impact of metal artefacts, but they considerably worsen detection of differences within the soft tissues themselves. This avoids the problems of overlapping structures, which considerably reduce the diagnostic ability of radiographs, particularly for soft tissue abnormalities. General principles Head and neck anatomy has often been considered one of the hardest areas to master. The complexity of the sensory organs, air intake, food intake and connection from the brain to the rest of the body, all in one of the thinnest areas of the body, makes it hard! There are a few basic rules to observe before attempting to use cross-sectional imaging to investigate a head and neck case. Although this artefact is apparently lessened using the bone reconstruction approach (b), and there is improvement in viewing bones, there is no improvement in the ability to interpret the soft tissues. Frequently in clinical imaging, students will diagnose invasion of cancers across boundaries that simply cannot be, and would be discovered to be absurd by simple examination of the oral cavity and throat. This is a tenant of all forensic image interpretation, even with improvements in photogrammetry: Imaging cannot replace thorough external examination of the body. In clinical work we go to great efforts to get the head and neck straight during scanning. For example, the jugular vein is bigger on the right, cerebral venous drainage not symmetrical and the tonsils can be very different. The axial scan plane is shown by the dashed line (a), (b) Images with the gantry in a standard position, so the X-ray beam passes vertically (large arrow). Images (a) and (c) show that the streak artefact from metal fillings in the teeth (short arrows) follows the line of the X-ray beam.
|