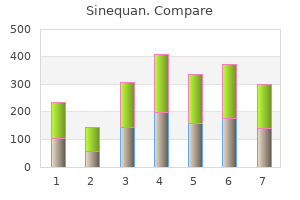
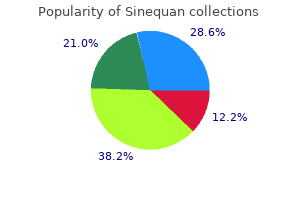
Sinequan"Order sinequan with mastercard, anxiety symptoms cures". By: V. Kirk, M.A., M.D., Ph.D. Associate Professor, Ohio University Heritage College of Osteopathic Medicine They should be used with extreme caution or not at all in patients with renal or cardiovascular disease anxiety heart rate buy sinequan 10mg mastercard. Despite the promise for these drugs, well-performed placebo-controlled trials have had disappointing results. Many patients with osteoarthritis use alternative therapies in an attempt to relieve their suffering. These agents appear to significantly alleviate pain and suffering by an unknown mechanism. Acupuncture, although used by many patients, appears to be no better than sham needling in controlled trials,5 and it is not without its own risks, which include reports of hepatitis transmission and pneumothoraces. NarcoticAnalgesics Narcotic analgesics should be reserved for patients with severe joint disease and intolerable suffering who are not candidates for other Less-potent medications, such as the new combination tramadol/ acetaminophen, should be tried first, reserving narcotic medications for those who still have severe pain. Usual precautions should be taken when prescribing these, such as counseling patients about their correct use and addictive potential. Treatment of depressive symptoms in older adults with arthritis resulted in significantly less pain and depression and overall improvement in health and quality of life. Arthroplasty is now used to treat many patients with severe osteoarthritis, especially those who are appropriate surgical candidates and for whom more-conservative measures have failed. Joint replacements can wear out after an average of 10 to 15 years, although some patients do well for much longer. Newer components and improved techniques might increase the longevity of these replacements in the future. Reoperation after the original replacement surgery may be more complex and can have higher failure and infection rates. Richy F, Bruyere O, Ethgen O, et al: Structural and symptomatic efficacy of glucosamine and chondroitin in knee osteoarthritis: A comprehensive meta-analysis. Many patients can achieve significant relief of their symptoms with appropriate care. Current therapies are being investigated to see if they improve the long-term outcomes of this disease. Ongoing research is aiming to identify patients who have a more rapidly progressive illness, and it is evaluating disease-specific molecular pathways as potential new targets for intervention. Advances in joint replacement surgery have made this an excellent treatment for many patients with more-severe disease. Correct diagnosis requires a high degree of suspicion coupled with knowledge of other diseases that can masquerade as vasculitis. By 1986, only 46 cases had been reported in the English-language medical literature. Since 1975, an increasing number of cases have been described, and 99 cases were reported through 1990. However, the final pathway of inflammation leads to occlusion of the involved blood vessel, thrombosis, and, ultimately, ischemia and necrosis of the territories of the involved vessels. Viral particles have been identified in the cytoplasm and nuclei of smooth muscle cells within the walls of affected vessels. By virtue of its angiographic diagnosis, few cases have included brain biopsies, and these have been uniformly unrevealing. The reversibility of the angiographic findings suggests a vasospastic process rather than a true arteritis. It is characterized by a long prodromal period, usually of 6 months or longer, and few patients present acutely. The most common manifesting signs and symptoms are headaches and mental status changes. Signs and symptoms of systemic vasculitis, such as peripheral neuropathy, fever, weight loss, or rash are usually lacking. The distinction between the two subsets is generally not difficult to recognize because signs and symptoms are sharply different (Table 2). The most common manifesting symptom was headache, which occurred in 14 of the 16 (88%), followed by focal symptoms in 10 (63%), and diffuse symptoms in 7 (44%) (see Table 1). Follow-up cerebral angiography, performed in 10 out of 16 (63%) of the patients, revealed total and near-total resolution of changes in all patients. This suggests that reversibility of the angiographic findings at the follow-up study is essential to securing the diagnosis.
Suggested Readings American Psychiatric Association: Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders anxiety wrap buy cheapest sinequan, 4th ed, text rev. Long-term outcome is best in motivated patients who participate in 12-step recovery programs and are free from other psychiatric disorders. Patients at risk for alcohol withdrawal should be referred to an inpatient chemical dependency program. Because of the high risk suffered by persons with a family history of addiction, family education during addiction treatment is essential. Patients in addiction treatment who have children or are planning to have children should be counseled to discourage alcohol exposure in their children. Patients struggling with other psychiatric disorders that place them at risk for developing an alcohol-use disorder should be advised to abstain from alcohol for the duration of their psychiatric treatment. Strict application of diagnostic criteria has been associated with a mean prevalence of 5% to 7% across studies of children and adolescents. This points to the fundamental problem of employing a descriptive nosology to define clinical disorders. Trouble sitting still, frequent fighting, temper outbursts, tendency to daydream, or suboptimal school performance is typical. School performance records or collateral information from parents can be very helpful. Published questionnaires can be used to capture the necessary information and can assist with (but not confirm) the diagnosis (Box 2). Neuropsychological testing can be used to determine whether or not a learning disability is present. Although neuroimaging and genetic testing offer attractive diagnostic potential, they are not sufficiently specific or sensitive for routine clinical use. Genes studied include those relevant to production of proteins involved in dopamine synthesis (dopa decarboxylase, the enzyme responsible for conversion of l-dopa to dopamine), inactivation (the dopamine and norepinephrine transporters), and degradation (catechol-O-methyltransferase) and in dopamine receptor activity (especially the dopamine D4 receptor). Blurts out answers before questions are completed Has difficulty awaiting turn (impatient) Interrupts or intrudes on others. Situational Notes Symptoms might not be observable when the patient is in highly structured or novel settings, engages in interesting activity, receives oneon-one attention or supervision, or is in a situation with frequent rewards for appropriate behavior. Symptoms typically worsen in situations that are unstructured, minimally supervised, or boring or that require sustained attention or mental effort. In adolescents (or adults), symptoms include restlessness (rather than hyperactivity, as seen in children), impaired academic performance, low self esteem, poor peer relations, and erratic work record. Hyperactivity Fidgets with hands or feet and squirms in seat Leaves seat in classroom or other situations where remaining seated is expected Adapted from American Psychiatric Association: Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 4th ed, text rev. If patient reports, alludes to , or exhibits signs or symptoms in one of the three categories. Adding life-skills coaching or cognitive-behavioral therapy, or both, in either individual or group settings can further improve outcome, but by themselves they are generally insufficient. The patient with a history of cardiovascular abnormalities, in particular structural heart disease. Treatment of such patients should involve close collaboration with an internist or cardiologist. Medication adjustments can be made by telephone or e-mail between office visits if necessary. Their therapeutic effect is associated with enhancement of central dopaminergic and noradrenergic activity. Dose the dosage of medication must be individualized by increasing gradually to maximal benefit while avoiding side effects. Clinical experience suggests a fine line between too little and too much medication. Clinical effects are felt within 15 to 30 minutes of oral administration, and peak blood levels are achieved within approximately 2 hours. The nonstimulants work more gradually and can take days to weeks to achieve a full therapeutic effect.
Typically anxiety symptoms 6 dpo purchase generic sinequan on-line, the fluid in serous inflammation does not contain microbes or large numbers of leukocytes (which tend to produce purulent inflammation, described later). Conversion of the fibrinous exudate to scar tissue (organization) within the pericardial sac leads to opaque fibrous thickening of the pericardium and epicardium in the area of exudation and, if the fibrosis is extensive, obliteration of the pericardial space. In time the abscess may become walled off and ultimately replaced by connective tissue. Ulcers An ulcer is a local defect, or excavation, of the surface of an organ or tissue that is produced by the sloughing (shedding) of inflamed necrotic tissue. Ulceration can occur only when tissue necrosis and resultant inflammation exist on or near a surface. It is most common in (1) the mucosa of the mouth, stomach, intestines, or genitourinary tract, and (2) the skin and subcutaneous tissue of the lower extremities in individuals with disorders that predispose to vascular insufficiency, such as diabetes, sickle cell anemia, and peripheral vascular disease. Ulcerations are best exemplified by peptic ulcer of the stomach or duodenum, in which acute and chronic inflammation coexist. During the acute stage there is intense polymorphonuclear infiltration and vascular dilation in the margins of the defect. With chronicity, the margins and base of the ulcer develop fibroblastic proliferation, scarring, as well as the accumulation of lymphocytes, macrophages, and plasma cells. Purulent (Suppurative) Inflammation and Abscess Purulent inflammation is characterized by the production of pus, an exudate consisting of neutrophils, the liquefied debris of necrotic cells, and edema fluid. The most frequent cause of purulent (also called suppurative) inflammation is infection with bacteria that cause liquefactive tissue necrosis, such as staphylococci; these pathogens are referred to as pyogenic (pus-producing) bacteria. Abscesses are localized collections of pus caused by suppuration buried in a tissue, an organ, or a confined space. Abscesses have a central liquefied region composed of necrotic leukocytes and tissue cells. Acute inflammation 95 Outcomes of Acute Inflammation Although, as might be expected, many variables may modify the basic process of inflammation, including the nature and intensity of the injury, the site and tissue affected, and the responsiveness of the host, acute inflammatory reactions typically have one of three outcomes. In a perfect world, all inflammatory reactions, once they have succeeded in eliminating the offending agent, would end with restoration of the site of acute inflammation to normal. This is called resolution and is the usual outcome when the injury is limited or short-lived or when there has been little tissue destruction and the damaged parenchymal cells can regenerate. Resolution involves removal of cellular debris and microbes by macrophages and resorption of edema fluid by lymphatics, followed by regeneration of the damaged tissue. This occurs after substantial tissue destruction, when the inflammatory injury involves tissues that are incapable of regeneration, or when there is abundant fibrin exudation in tissue or in serous cavities (pleura, peritoneum) that cannot be adequately cleared. In all these situations, connective tissue grows into the area of damage or exudate, converting it into a mass of fibrous tissue, a process also called organization. Acute to chronic transition occurs when the acute inflammatory response cannot be resolved, as a result of either the persistence of the injurious agent or some interference with the normal process of healing. When a host encounters an injurious agent, such as a microbe or dead cells, resident phagocytes and phagocytes recruited from the blood try to eliminate these agents. At the same time, phagocytes and other host cells react to the presence of the foreign or abnormal substance by liberating cytokines, lipid messengers, and other mediators of inflammation. Some of these mediators act on small blood vessels in the vicinity and promote the efflux of plasma proteins and the recruitment of circulating leukocytes to the site where the offending agent is located. The recruited leukocytes are activated by molecules derived from microbes and injured cells and by locally produced mediators, and the activated leukocytes try to remove the offending agent by phagocytosis. As the injurious agent is eliminated and antiinflammatory mechanisms become active, the process subsides and the host returns to a normal state of health. If the injurious agent cannot be quickly eliminated, the result may be chronic inflammation. The vascular and cellular reactions account for the cardinal signs of inflammation: rubor, calor, tumor, dolor, and functio laesa. The increased blood flow to the injured area and increased vascular permeability lead to the accumulation of extravascular fluid rich in plasma proteins, known as edema. The redness (rubor), warmth (calor), and swelling (tumor) are caused by the increased blood flow and edema. In these diseases, autoantigens evoke a self-perpetuating immune reaction that results in chronic tissue damage and inflammation; examples of such diseases include rheumatoid arthritis and multiple sclerosis.
A new patch should be applied every week for 3 weeks anxiety symptoms dsm order online sinequan, followed by 1 patch-free week. The patch exposes women to higher levels of estrogen than most oral hormonal contraceptive pills. Application sites include the buttocks, abdomen, outer arms, and torso, except the breasts. The patch may be a good option for women who have difficulty adhering to other hormonal contraceptive regimens. Physicians must balance the higher estrogen exposure against the chance of pregnancy. If the patch-free interval exceeds 2 days, pregnancy should be ruled out, a new patch should be placed, and a backup contraceptive method should be used for 7 days. In case of skin irritation, the patch should be removed and a new patch applied to another site. Women weighing more than 198 pounds should not use the patch because its effectiveness is reduced. The outer diameter of the ring is 54 mm, and the cross-sectional diameter is 4 mm. The ring can be inserted at any time during the first 5 days of the menstrual cycle. If the ring is expelled during the first 3 weeks of use, it should be washed with lukewarm water and then replaced. If the ring-free interval is longer than 3 hours, a backup contraceptive method If the ring is left in place, pregnancy should be ruled out before a new ring is inserted, and a backup method should be used for 7 days after inserting a new ring. The vertical stem contains a mixture of silicone and 52 mg of levonorgestrel surrounded by a Silastic capsule. This device causes changes in the lining of the uterus so that the fertilized egg cannot implant, and it thickens the cervical mucus to make sperm entry difficult. Side effects include cramping during insertion, bleeding, pelvic inflammatory disease, and perforation of the uterus. Spontaneity is maintained, and there are marked reductions in menstrual blood loss and dysmenorrhea. The risk of pelvic infection is higher during the first 20 days of Mirena insertion. It fits securely in the vagina, covering the cervix, and must be fitted by a physician. It has a one-way valve that creates suction by venting trapped air between the shield and cervix. Resizing should be done after abdominal or pelvic surgery, after any pregnancy longer than 14 weeks, and after any significant weight change. To protect against pregnancy, the devices should be left in place for a certain minimum of time after intercourse and then removed to decrease risk of infection. ContraceptiveSponge the Today Sponge, a nonhormonal contraceptive spermicidal sponge is now back on the market for over-the-counter purchase. The effectiveness of the Today sponge when used appropriately and consistently is 89% to 91%. It requires no special fitting, becomes effective immediately after insertion, and protects against pregnancy for the next 24 hours without the need of additional spermicide. The Today sponge should be kept in place for 6 hours after intercourse to ensure effective contraception. One ring is inserted into the vagina much like a diaphragm, while the other remains outside, covering the labia. The male and female condoms should not be used at the same time because they will not both stay in place. The first pill should be taken as soon as possible within 72 hours of unprotected intercourse. The Yuzpe regimen, marketed as Preven, is no longer available in the United States. Cheap 25mg sinequan with mastercard. Xanax (Alprazolam) Side Effects - Full List of Side Effects Dangers What to expect....
|