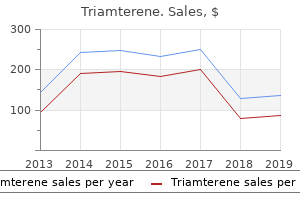
Triamterene"Buy triamterene once a day, blood pressure pregnancy range". By: K. Nerusul, M.B. B.CH. B.A.O., Ph.D. Vice Chair, Universidad Central del Caribe School of Medicine The neurologic effects of oxaliplatin appear to be cumulative in that they become more pronounced and of greater duration with successive cycles; however arteria definicion order triamterene in india, unlike those of cisplatin, they are reversible with drug cessation. The persistence of the neurotoxicity has led to approaches to ameliorate it, including the use of protective agents. The use of calcium and magnesium salts intravenously before and after each infusion has been shown to be ineffective. Myelosuppression is uncommon and is not severe with oxaliplatin as a single agent, but it is a feature of combinations including this drug. The drug is most toxic to the platelet precursors, but neutropenia and anemia are frequently observed. The lowest platelet counts after a single dose of carboplatin are observed 17 to 21 days later, and recovery usually occurs by day 28. The effect is dose dependent, but individuals vary widely in their susceptibility. Both groups derived pharmacologically based formulas to predict toxicity and guide carboplatin dosing. Patients who are elderly, have a poor performance status, or have a history of extensive pretreatment have a higher risk of toxicity even when dosage is calculated with these methods, but the safety of drug administration has been enhanced. Dosages some 30% higher than those using a dosing strategy based solely on body surface area may safely be used. A determination of whether this approach to dosing improves outcomes will require a randomized trial. The other toxicities of carboplatin are generally milder and better tolerated than those of cisplatin. Nausea and vomiting, although frequent, are less severe, shorter in duration, and more easily controlled with standard antiemetics. High dose cis-platinum diamine dichloride: amelioration of renal toxicity by mannitol diuresis. Initiatives with platinum- and quinazoline-based antitumor molecules-Fourteenth Bruce F. Examination of antitumor activities of platinum complexes of 1,2-diaminocyclohexane isomers and their related complexes. Structure-activity relationships within diand trinuclear platinum phase-I clinical anticancer agents. Cell surface-directed interaction of anthracyclines leads to cytotoxicity and nuclear factor kappaB activation but not apoptosis signaling. Mesenchymal stem cells induce resistance to chemotherapy through the release of platinum-induced fatty acids. Copper transporter 2 regulates the cellular accumulation and cytotoxicity of cisplatin and carboplatin. The relationship between nuclear glutathione levels and resistance to melphalan in human ovarian tumour cells. High resistance to cisplatin in human ovarian cancer cell lines is associated with marked increase in glutathione synthesis. Enhanced cisplatin cytotoxicity by disturbing the nucleotide excision repair pathway in ovarian cancer cell lines. Olaparib in patients with recurrent high-grade serous or poorly differentiated ovarian carcinoma or triplenegative breast cancer: a phase 2, multicentre, open-label, non-randomised study. Autophagy inhibition enhances therapyinduced apoptosis in a Myc-induced model of lymphoma. Prediction of carboplatin clearance from standard morphological and biological patient characteristics. Relationships between carboplatin exposure and tumor response and toxicity in patients with ovarian cancer. Aminopterin was the first antimetabolite with documented clinical activity in the treatment of children with acute leukemia in the 1940s. This agent is presently approved for the treatment of relapsed or refractory peripheral T-cell lymphomas. Gene amplification is a common resistance mechanism observed in various experimental systems, including tumor samples from patients. This acute induction of target protein in response to drug exposure is mediated, in part, by a translational regulatory mechanism, which may represent a clinically relevant mechanism for the acute development of cellular drug resistance. It is advisable to evacuate these fluid collections before treatment and monitor plasma drug concentrations closely.
Genetic testing and cancer risk management recommendations by physicians for at-risk relatives keeping blood pressure chart cheap triamterene 75mg without a prescription. Efficacy of bilateral prophylactic mastectomy in women with a family history of breast cancer. Points to consider: ethical, legal, and psychosocial implications of genetic testing in children and adolescents. American Society of Human Genetics Board of Directors, American College of Medical Genetics Board of Directors. These panels simultaneously analyze groups of genes that contribute to increased risk for breast, colon, ovarian, uterine, and other cancers. Because testing for these genes is new to the clinical setting, it is expected to take several years to compile accurate cancer risk estimates and appropriate recommendations for surveillance and risk reduction. Furthermore, the rate of variants of uncertain significance will likely be more common in the lesser known genes. In response, several state and one national insurance company have mandated genetic counseling by certified providers before they will cover cancer genetic testing. First, results rather than plausible reasoning are required to support conclusions. Second, in an experiment the treatments are assigned so that one can conclude that differences in outcome are due to differences in treatment effect. In observational studies, treatments are not assigned as part of the study, so differences in outcome between treatment groups may merely result from the fact that sicker patients received less intensive treatments. Experiments should be prospectively planned and conducted under controlled conditions to provide definitive answers to well-defined questions. Using tumor registry data to compare the survival rates of patients with prostate cancer treated with surgery to those of patients receiving radiotherapy is an example of an observational study, not a clinical trial. Treatment assignments, staging workup, and followup procedures are out of the control of the investigators, and are conducted with no considerations about the validity of the subsequent attempt at comparison. The statistical associations resulting from such studies are, consequently, a weak basis for causal inferences about relationships between the treatments administered and the outcomes observed. Surprisingly, this does not seem to be realized by the politicians and health-care administrators allocating enormous sums of money to outcomes research based on electronic medical records from general practice. In such observational studies, treatments are usually selected on the basis of subjective assessment of the prognosis of the patient, specialties of the physician, and diagnostic evaluations. Unknown patient selection factors generally are more important determinants of patient outcome than are differences between treatments. For example, Subramanian and Simon1 found that in observational studies that developed gene expression prognostic signatures for patients with early stage nonsmall-cell lung cancer, those who received chemotherapy had poorer survivals than those who did not even after adjusting for all recorded prognostic factors. It also should define the specific questions to be answered by the study and should directly justify that the number of patients and the nature of the controls are adequate to answer these questions. Some clinical trials are really only guidelines for clinical management supplemented by lofty objectives with no scientific meaning and no realistic chance of providing a reliable answer to a well-defined medical question. Such studies are a disservice to the patients who are undergoing some inconvenience to contribute to the welfare of future patients. Patients with advanced disease that is resistant to standard therapy but who have normal organ function are usually included in such trials. Phase 1 trials are usually initiated at a low dose that is not expected to produce serious toxicity. A starting dose of onetenth the lethal dose (expressed as milligrams per square meter of body surface area) in the most sensitive species usually is used. Dose escalation for subsequent patients occurs only after sufficient time has passed to observe acute toxic effects for patients treated at lower doses. The second level is twice the starting dose, the third level is 67% greater than the second, the fourth level is 50% greater than the third, the fifth is 40% greater than the fourth, and each subsequent step is 33% greater than that preceding it. They provide very limited information about interpatient variability and cumulative toxicity. At that point, acceleration ceases and standard cohorts of three to six patients with 40% dose-step increments are used.
Adoptive Cell Transfer Immunotherapy Adoptive cellular immunotherapy refers to the transfer to the tumor-bearing host of immune lymphocytes with anticancer activity heart attack vs panic attack buy 75mg triamterene visa. There was no difference in the time to disease progression; however, the vaccine group had a median survival of 25. Tumors are resected and individual cultures are grown and tested for antitumor reactivity. Optimal cultures are expanded in vitro and reinfused into the autologous patient who had received a preparative lymphodepleting chemotherapy. These cells can be activated in vitro and thus are not subjected to the tolerizing influences that exist in vivo. Perhaps, most important, the host can be manipulated prior to the transfer of the anticancer cells to provide an optimal tumor microenvironment free of in vivo suppressive factors. The administration of a preparative lymphodepleting chemotherapy regimen, consisting of cyclophosphamide and fludarabine with or without 2 or 12 Gy total body irradiation, could substantially enhance the survival and persistence of the transferred cells and increase their in vivo antitumor effectiveness. Only 1 of these 20 patients has recurred, and the remaining patients have ongoing complete regressions from 80 to over 104 months Table 14. The results of three consecutive trials using different preparative regimens have been combined in this analysis. Of 20 patients who achieved a complete cancer regression, only one has recurred with a median followup of over 8 years. This approach has now been utilized to identify T cells used to successfully treat a patient with chemotherapy-refractory cholangiocarcinoma and provides a blueprint for the application of cell transfer therapy for a variety of common epithelial cancers. The first is the selection of an appropriate gene transfer method in order to achieve high receptor expression levels in the transferred T cells. For this discussion, we will consider both nonviral and viral-based gene delivery platforms. Generally speaking, there are two categories of nonviral gene transfer, chemical and physical. Currently, it is not clear if stable long-term receptor expression is required to mediate tumor regression. However, the main criticism of the non-viral methods described is the lack of stable gene transfer. To overcome this problem, many investigators are now using transposons such as sleeping beauty or piggybac. Gammaretroviral vectors have been used in human clinical applications for over 20 years. This platform is easily scaled up to support large-scale vector production efforts. An alternative to the gammaretroviral vector platform is the lentiviral vector platform. There are some advantages to selecting a lentiviral vector for T-cell engineering in that one can transduce large numbers of minimally stimulated T cells,148 transfer more complex and larger gene expression cassettes, and yield a potentially safer chromosomal integration profile as compared to gammaretroviruses. Nine of 19 patients (47%) with synovial cell sarcoma showed objective tumor response, only one of which is complete and ongoing at 12 months. In a trial conducted at the National Cancer Institute, Surgery Branch, Kochenderfer et al. Significant toxicity, including hypotension and neurologic toxicity, occurred during this clinical trial. Autoimmunity correlates with tumor regression in patients with metastatic melanoma treated with anti-cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen-4. A gene encoding an antigen recognized by cytolytic T lymphocytes on a human melanoma. One way to accomplish this goal might be to genetically modify T cells to give them the ability to specifically recognize antigens expressed by malignant cells. T cells targeting carcinoembryonic antigen can mediate regression of metastatic colorectal cancer but induce severe transient colitis. Biological activity of recombinant human interleukin-2 produced in Escherichia coli. Prospective randomized trial of high-dose interleukin-2 alone or in conjunction with lymphokine-activated killer cells for the treatment of patients with advanced cancer. Results of treatment of 255 patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma who received high dose proleukin interleukin-2 therapy. Randomized study of high-dose and low-dose interleukin-2 in patients with metastatic renal cancer.
A novel approach in the treatment of cancer: targeting the epidermal growth factor receptor blood pressure chart tracker generic triamterene 75 mg. Cetuximab shows activity in colorectal cancer patients with tumors that do not express the epidermal growth factor receptor by immunohistochemistry. Accurate classification of these conditions is imperative, given their distinct cancer risks, management strategies, and consequent risk to relatives. However, overlapping features and atypical or attenuated presentations make diagnosis difficult in some cases. Determining the histologic types of colorectal polyps identified is especially useful in guiding diagnostic strategies. Genetic testing is now available for these conditions and, in most cases, allows for a precise diagnosis. Adenomatous polyps of the duodenum (20% to 100%) and the periampullary region (at least 50%) are common. They are typically small (1 to 5 mm), sessile, and usually asymptomatic and are located in the fundus and body of the stomach. In addition, there are increased risks for other cancers, including those of the pancreas, thyroid, bile duct, brain (typically medulloblastoma), and liver (specifically hepatoblastoma). This creates diagnostic difficulties when evaluating an individual with moderate adenomatous polyposis. Colonoscopies in 120 mutation-positive individuals within the same family revealed that 37% had less than 10 adenomatous colon polyps (average age, 36 years; range, 16 to 67 years), 28% had 10 to 50 polyps (average age, 39 years; range, 21 to 76 years), and 35% had greater than 50 polyps (average age, 48 years; range, 27 to 49 years). After polyps become too numerous (usually >20 to 30 polyps) to manage endoscopically or when adenomas with advanced histology are identified, a prophylactic colectomy is advised. Genetic testing has also been shown to be cost-effective,16 although it is unlikely to change colon management for cases with extensive adenomatous polyposis. Serrated polyps include hyperplastic polyps, sessile serrated polyps (also referred to as sessile serrated adenomas), and traditional serrated adenomas. In addition, three met the criteria for hyperplastic polyposis, now known as serrated polyposis. The World Health Organization diagnostic criteria for serrated polyposis include an individual with any of the following: (1) at least five serrated polyps proximal to the sigmoid colon with at least two larger than 10 mm; (2) greater than 20 serrated polyps of any size, but distributed through the colon; and (3) any number of serrated polyps proximal to the sigmoid colon in an individual with a first-degree relative with serrated polyposis. By the age of 20 years, 50% of individuals present with small-bowel obstruction, intussusception, and/or bleeding due to small-bowel polyps. They are rare, account for a minority of all colon polyps, and can be a red flag for an underlying cancer predisposition syndrome. When hamartomatous polyps are found in an individual, the differential diagnosis depends, in part, on the histologic type, total number, and age at onset of the polyps. Hamartomas can often be misdiagnosed as other polyp types, and therefore, review by a gastrointestinal pathologist should be considered. Simplified guidelines for referral for genetic counseling include individuals with any of the following: (1) greater than 10 colonic adenomas, (2) three or more hamartomatous polyps, or (3) at least one PeutzJeghers polyp. Other manifestations in these individuals may help target genetic testing to a specific condition. Once the genetic cause has been identified in an affected individual, predictive testing in at-risk relatives is critical. Family members who test negative can be spared the increased surveillance and risk-reducing procedures that are warranted for family members who test positive. It is important that health-care providers involved in the care of patients with hereditary colonic polyposis conditions stay updated with management guidelines because recommendations are constantly evolving. Screening guidelines and premorbid diagnosis of familial adenomatous polyposis using linkage. Genetic testing and phenotype in a large kindred with attenuated familial adenomatous polyposis. Surveillance and management of upper gastrointestinal disease in familial adenomatous polyposis. Gastric adenocarcinoma arising from fundic gland polyps in a patient with familial adenomatous polyposis syndrome. A nation-wide study comparing sporadic and familial adenomatous polyposis-related desmoid-type fibromatoses. Generic triamterene 75 mg free shipping. SUPER HIGH BLOOD PRESSURE BROS. 3D.
|