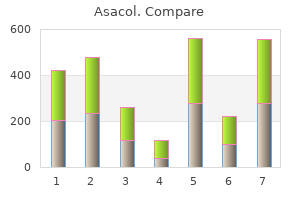
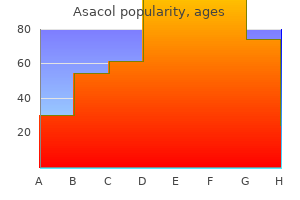
Asacol"Order discount asacol line, treatment of uti". By: T. Fasim, M.A., M.D., M.P.H. Deputy Director, UAMS College of Medicine A Cochrane review of lactational amennorhoea for family planning concluded that a wiser approach to the post-partum period would be to encourage breastfeeding and symptoms of appendicitis purchase cheap asacol on line, in addition, to motivate the mother to use an alternative form of contraceptive, other than lactational amenorrhoea, if contraception is required (Van der Wijden et al. Emergency contraception the most widely used emergency contraceptive uses levonorgestrel at either a single high dose of 1500 micrograms, or two doses of 750 micrograms taken 12 hours apart, within a 72-hour window of unprotected sexual intercourse. As a progesterone-only preparation there are no contraindications to use in renal disease, hypertension, coagulopathy, and lupus. In addition, there is no evidence of an increase in cardiovascular complications (Faculty of Sexual and Reproductive Healthcare, 2009). Drugs Patients with renal disease can be prescribed a variety of different long-term and short-term medications. How glucocorticoids control their own strength and the balance between pro- and anti-inflammatory mediators. Effects of depot medroxyprogesterone acetate on bone density and bone metabolism before and after peak bone mass: a case-control study. Poststerilization regret: findings from the United States collaborative review of sterilization. Oral contraceptives and venous thromboembolism: a five-year national case-control study. Hormonal contraception and risk of venous thromboembolism: national follow-up study. Copper-T intrauterine device and levonorgestrel intrauterine system: biological bases of their mechanism of action. The contraceptive vaginal ring in women with renal and liver transplantation: analysis of preliminary results. Renal hemodynamic and tubular responses to salt in women using oral contraceptives. Oral and transdermal hormonal contraception in women after kidney transplantation. It is proposed that predominance of right-sided hydronephrosis is due to dextrorotation of the uterus, and/or the left ovarian vein crossing the right ureter at the pelvic brim. Pelvicalyceal dilatation has usually resolved by 6 weeks post partum but one report suggested that two out of 20 women have persistent ureteric dilation (Fried et al. Though these changes can create diagnostic challenges they are asymptomatic and of no significance, but urinary stasis increases the risk of bacteriuria, and pyelonephritis in pregnancy. It is speculated that 24-hour urine collections may be affected by incomplete emptying of the ureters, and recommended that women should lie on their side for an hour before and after the end of a collection, but practically this is challenging. The mechanisms underlying these changes in glomerular filtration are unclear, but may be associated with the peptide hormone relaxin released by the corpus luteum, levels of which increase in the luteal phase (Stewart et al. Urinary symptoms in pregnancy Women commonly report increased urinary frequency in early pregnancy associated with nocturia, which may be due to the effects of progesterone, and increased fluid intake (FitzGerald and Graziano, 2007). In later pregnancy, the distension of the bladder is physically limited by pelvic crowding, and urinary frequency may recur. The right ureter is abruptly cut off at the pelvic brim where it crosses the iliac artery (the so-called iliac sign). The solid line represents the mean and the stippled area the range for nine women with successful obstetric outcome. Calculated from the data of Davison and Hytten (1975), Dunlop (1976), Ezimokhai et al. Changes in systemic physiology after conception Marked physiological adaptations occur during pregnancy. Despite increased cardiac output there is an overall reduction in mean arterial blood pressure. Substantial changes in systemic and renal vasodilation have occurred by 6 months (Chapman et al. In addition there is an increase in plasma volume of up to 50% of non-pregnant values, which is maximal during the second trimester.
Those with severe symptoms only partially alleviated by antihistamines medications used to treat schizophrenia discount asacol 800mg mastercard, topical anti-inflammatory agents, and environmental controls and those with perennial symptoms who require daily therapy should be referred for specific IgE testing. Desensitization (allergy shots) is an effective treatment for patients who are not well controlled with medications or who prefer not to use them regularly. In general, lower airway obstruction produces prolongation of the expiratory phase of respiration and typical expiratory wheezing, whereas upper airway obstruction prolongs the inspiratory phase. Wheezing is defined as musical or whistling auscultatory sounds heard more often on expiration than on inspiration, although in severe obstruction both inspiratory and expiratory wheezing are often present. Stridor is defined as a crowing sound usually heard during the inspiratory phase of respiration. It tends to be loud when the obstruction is subglottic and quiet when obstruction is supraglottic. Mild to moderate increases in respiratory and heart rates are common in upper airway obstruction, whereas lower airway disorders such as pneumonitis and asthma often lead to markedly increased respiratory and heart rates. Retractions are often generalized (suprasternal, intracostal, and subcostal) in severe airway obstruction of any etiology. Asthma Asthma is the most common chronic respiratory condition affecting children. In childhood, boys are affected more often than girls and tend to have more severe disease. Beyond puberty, the gender distribution is equal, because onset in the teenage years is more common in girls, perhaps due to hormonal factors involved in menarche. Asthmatic children with respiratory allergy and eczema usually have more severe courses than those who wheeze only with upper respiratory infections. After a rising trend from 1980s to 1990s, death rates due to asthma have recently declined. However, there remains a great deal of racial disparity in childhood asthma, with African-American children having higher mortality compared to Caucasian children. It has been noted that prevalence increases with age, but health care utilization is highest among the youngest children affected. Respiratory Disease Respiratory Distress Respiratory distress in children (tachypnea with or without grunting, flaring, retractions, and cyanosis) should be promptly evaluated and treated. The first step in approaching respiratory distress is to differentiate upper from lower airway disorders. At times, various degrees of upper and lower airway obstruction may coexist, as in laryngotracheobronchitis. The last is characterized by inherent hyperreactivity of the airways to stimuli, including allergens, infection, exercise, chemical agents (such as methacholine), cold or dry air, emotions, and weather changes. Specific allergens implicated in atopic patients are pollen, mold spores, house dust mites, and animal dander, whereas drugs, food, and insect venoms typically cause similar symptoms of wheezing and respiratory distress as part of anaphylaxis (see earlier discussion). On exposure, these allergens, via cross-linking specific IgE, produce the characteristic features of asthma: mucosal edema, increased mucus production, and smooth muscle contraction that result in airway inflammation, airway hyperreactivity, and bronchoconstriction. These responses combine to produce a state of revers- ible obstruction of the large and small airways that is the hallmark of asthma. Patients with asthma should be evaluated to determine the important triggers for their disease. Affected individuals are often aware of the specific trigger for exacerbations of their asthma. Viruses are the most common precipitants of acute asthma in children, especially rhinoviruses, respiratory syncytial virus, and parainfluenza viruses. These infections usually affect the upper and lower airways, producing rhinorrhea, nasal congestion, and wheezing, which tends to develop insidiously. In contrast, allergen-triggered episodes typically lack fever and have a more abrupt onset of wheezing. The diagnosis of asthma, especially in younger children who cannot do pulmonary function tests, is frequently based on historical findings alone, indicating the importance of taking a thorough history. The frequency and severity of acute asthma episodes and the level of symptoms between episodes can be used to grade asthma severity and to guide therapy on the basis of published guidelines (Table 4. The early stages of an asthma exacerbation in children are characterized by the onset of cough, chest tightness, and chest retractions or audible wheezing. The parents should be educated to observe their child for the warning signs and identify the onset of asthmatic exacerbation at home. Buy online asacol. my eye is swollen and random chat. Saleem and Corinne Antignac 339 Cystinosis 2789 2798 328 Molecular basis of renal tumour syndromes Thomas Connor and Patrick H medicine disposal cheap 800mg asacol with amex. Bissler Neil Turner, Teena Tandon, and Rajiv Agarwal Neil Turner and Bertrand Knebelmann 331 Hypoxia-inducible factor and renal disorders 2739 Thomas Connor and Patrick H. An underlying genetic diagnosis may be suspected because of a known family history. A detailed family history going back over at least three generations may provide a clue, and consanguinity is important to note as it increases the chance of an autosomal recessive disorder. The turnaround times for mutation screening and the costs involved are falling all the time, and in some cases molecular testing can replace invasive procedures such as renal biopsy, for example, in the diagnosis of Alport syndrome. It is important that nephrologists know that not all mutations within a gene are identifiable (some may be deeply hidden within an intron, for example), so a negative results does not exclude the diagnosis. Clinicians requesting genetic tests also need to be aware of the possibility of generating unexpected or un-interpretable information such as molecular variants of unknown significance or non-paternity. Properly accredited laboratories will do their best to provide an interpretation of results, and will be aided in reaching useful conclusions if they are provided with sufficient clinical information; but help from clinical geneticists may also be required. The important of making a genetic diagnosis It is important to make an accurate diagnosis in order to optimize health and life expectancy; to identify other manifestation of a syndrome for which a patient should be screened; to establish the underlying pattern of inheritance so that recurrence risks can be determined and at-risk relatives offered screening; to enable a discussion of all possible reproductive options, if indicated; and to facilitate recruitment into treatment trials. Failure to make a genetic diagnosis may have adverse implications, not only for the proband, but also for relatives who are not aware that they are at risk of being affected or of passing the condition on to their children. Clinicians have a duty to be vigilant and consider the possibility of a genetic diagnosis, particularly if the use of a donated kidney from a living relative is being considered. Tests to diagnose genetic causes of renal disease A genetic diagnosis does not always require a molecular or cytogenetic test. The majority of cases of adult (autosomal dominant) polycystic renal disease are diagnosed following an ultrasound scan of the kidneys and many cases of Alport syndrome are diagnosed after tissue from a renal biopsy is examined under the electron microscope. Whether or not testing of genetic material is involved, clinicians must be aware of the responsibilities that are associated with making a genetic diagnosis, not only for the proband but also for relatives who may be affected or at risk. Primary diagnosis of renal disease will often be the role of the nephrologist, whilst counselling and testing of the extended family can be undertaken by clinical geneticists/genetic counsellors; nevertheless, nephrologists must discuss the implications of considering a genetic diagnosis in a Predictive testing versus diagnostic testing Diagnostic tests may confirm a suspected clinical diagnosis, for example, a patient presenting with symptoms and signs of renal failure may have a biopsy, ultrasound scan, or molecular test which provides a specific diagnosis. This then enables them to undergo regular surveillance to screen for manifestations of the condition that would benefit from early intervention. Patients in whom a mutation has been identified, whether they are symptomatic or not, can be offered prenatal diagnosis or pre-implantation genetic diagnosis, if appropriate. Predictive testing is normally offered in conjunction with genetic counselling so that the medical implications and also practical implications (for future employment and insurance purposes, for example) can be discussed. Whole-genome sequencing At present, exome capture and whole-genome sequencing techniques are often used on a research basis for discovering new candidate genes. However, the first clinical applications of so-called Next-Gen sequencing techniques are happening now. Ethical frameworks to deal with the new issues this will raise are not fully developed even in a research setting (Green et al. Some examples of the questions raised include the following: Genetic testing in childhood For conditions that are expected to manifest in childhood, or for which early intervention (pre-symptomatically) is indicated, it may be appropriate to perform genetic testing so that health surveillance or other specific management plans can be made. Young people in this position should be offered genetic counselling at an appropriate age (typically in their mid teens) so that they can explore the implications of their positive family history and make an informed decision about whether or not to undergo predictive testing. Some countries have legislation to protect people who have an inherited condition from discrimination. Whether to report incidentally discovered abnormalities of definite significance for health or life and for which there is an effective therapy. And what if there is not a preventive treatment, but possible significance for relatives Whether to report incidentally discovered abnormalities of uncertain significance. Whether to pass on information to other family members without the consent of the index patient. As knowledge expands in the years and decades after initial testing, how/whether to keep patients informed. This trend will continue and non-geneticists need to remain up to date with the range of tests available and understand clinically appropriate ways of using them, in order to exploit their clinical utility and enhance patient care. In conjunction with this lie responsibilities for understanding both the potential power and also the limitations of these tests, and the ethical implications of genetic testing for both the proband and their relatives. Genetic testing and patient pathways It is important that genetic tests are performed on the right person at the right time, with a clear understanding of the sort of information that may be expected and knowledge about how to interpret it.
However medications xarelto discount asacol 400mg fast delivery, when the warts are restricted to the hymen in a prepubertal child, sexual abuse is the likely source. A, Abrasions, contusions, and punctate tears of the perineum and perianal areas can be seen in this prepubescent girl. D, Acute bruising of the glans is seen in this baby, who also had a femur fracture. E, In this older boy, penile and scrotal bruising are evident along with multiple small bruises over the lower abdomen. F, Perianal lacerations, abrasions, and burns are apparent in this prepubescent boy. The examiner suspected that the burns were inflicted to obscure the evidence of sodomy. G, Prominent, perianal ecchymoses were found in this 3-year-old boy who had been sodomized. A, the hymen is almost completely absent, and the portion remaining has slightly thickened, rolled margins. B, this hymen has a posterior notch deeper than 50% of the rim, which persists in the knee/chest position (not shown here). C, Scarring, edema, and fresh excoriations of the perineal body extending to the anterior anal rim are seen in this child who was repetitively abused. D, the adhesed labia minora in another child are markedly thickened secondary to chronic frictional trauma incurred during sexual abuse. If a vaginal discharge is found in a patient presenting within 24 hours of sexual abuse, a wet mount may reveal sperm. A portion of the discharge should also be collected for acid phosphatase, blood grouping, and enzyme studies. In the very young child, genital herpes infections may be acquired through sexual contact but are more often the result of spread from oral or hand lesions from the patient, or from a parent with a cold sore, as a result of poor attention to handwashing. Perinatally acquired Trichomonas infection causes a copious vaginal discharge in the neonate, which abates even without treatment, although the organism can persist for months. In contrast, Chlamydia infection acquired in the neonatal period may persist for several years. Hence, finding this organism in the very young child cannot be considered diagnostic of sexual abuse. C, In the knee/chest position, narrowing and thickening of the hymenal rim can be seen more clearly. B, Coalescent and discrete condylomata are seen in the perianal area of this 4-year-old boy with a history of being sodomized. C, More extensive lesions involving the mons, the introitus, the labia, and perianal area developed in another child. Specimen Collection Laboratory studies are designed to augment the physical assessment of injury, identify sexually transmitted pathogens, and document the presence or absence of seminal fluid. Data confirm clinical experience that the yield for evidence of ejaculate on the body of a prepubertal patient presenting more than 24 hours after the abuse is extremely low. Hence studies to detect semen may be omitted if the patient seeks attention later than this. However, it is particularly important to collect articles of unlaundered clothing and bed linens that may have evidence of ejaculate on them, because semen may be retrieved from these items even months later. Unfortunately, this is often overlooked in the process of evidence collection in sexual abuse cases. Because the yield of positive results from vaginal specimens obtained from asymptomatic prepubertal victims is so low, the collection of specimens sometimes uncomfortable, and the cost high, many centers are advocating a more selective approach in obtaining cultures in this age group on the basis of the level of risk. The possibility of pregnancy must also be considered in all such patients, and a pregnancy test must be performed. However, if anal rape is reported or if anal inspection suggests evidence of forceful anal penetration with marked bruising or lacerations, especially in a prepubertal child who has clearly been traumatized emotionally and physically, rectal examination should be deferred until the patient is sedated before full anesthetic administration in the operating room.
|