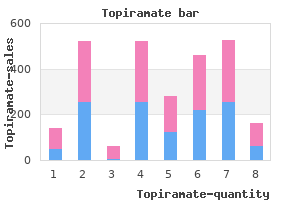
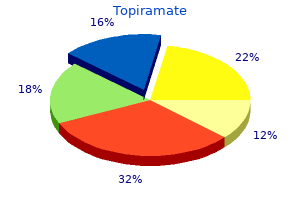
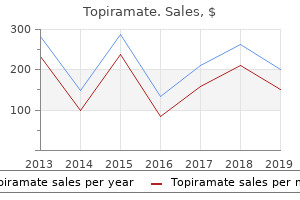
Topiramate"Order topiramate 100 mg with mastercard, medicine x protein powder". By: F. Tarok, M.A., M.D., M.P.H. Clinical Director, The Ohio State University College of Medicine The control of limbs proceeds in a proximal to distal manner medications names 100 mg topiramate, such that hand use is learnt before control over fingers. Certain primitive reflexes have to be lost before relevant milestones are attained. For example, palmar grasp is lost before voluntary grasp is attained and the asymmetric tonic neck reflex has to disappear to allow the child to turnover. The initial disorganized mass activity is gradually replaced by specific and wilful actions. Hence, when shown a bright toy, a 3-4 month old squeals loudly and excitedly moves all limbs, whereas a 3-4 yr old may just smile and ask for it. Factors Affecting Development Development depends on a variety of mutually interactive factors such as hereditary potential, biological integrity, physical and psychosocial environment and emotional stimulation. The brain matures through a dynamic interplay of genetic, biological and psychosocial factors. Infancy and early childhood are the most crucial phases during which development takes place. Appropriate sensory inputs through hearing and vision, a secure environment and responsive parenting provide the bases for healthy patterns of learning, behavior and health. Poverty is among the most important risk factors associated with poor development. Poverty expo ses the child to many other risk factors such as lack of stimulation or excessive stress, malnutrition, exposure to environmental toxins, and concurrent diseases that adver sely affect development. Moreover, certain developmental patterns are observed to follow parental patterns like speech. Prenatal Factors Genetic factors Intelligence of parents has direct Prematurity Babies born before 37 weeks of gestation are more likely to have developmental impairment compared to term counterparts with babies born before 32 weeks gestation being at the highest risk. Premature babies are at risk due to complications, including intracranial bleed, white matter injury, hypoxia, hyperbilirubinemia and hypoglycemia. Postneonatal Factors Infant and child nutrition Severe calorie deficiency, as evident by stunting, is associated with apathy, depressed affect, decreased play and activities and insecure attach ment. Calorie deficiency is often associated with deficiency of multiple micronutrients and vitamins (including zinc, vitamins A, B12, D, E, riboflavin and iodine) that contribute to developmental impairment. Linear growth retardation or stunting occurs in nearly one-third of children aged less than 5 yr in low-income and middle-income countries. There is positive association between early height-for-age and cognitive or language ability, rates of school enrolment and grades attained by late adolescence and formal employment at age 20-22 yr. Increase in weight to cause a change by one standard deviation from birth to 24 months was associated with increased rates of schooling and inversely related to grade failures. Macronutrient supplementation to promote better growth consistently shows concurrent developmental benefits. Iron deficiency Iron deficiency has been shown to be associated with electrophysiological evidence of delayed brain maturation, poorer cognitive, motor and social emotional development in infancy and early childhood. Iodine deficiency Iodine is a constituent of thyroid hormones, which affect central nervous system develop ment and regulate many physiological processes. Iodine deficiency can lead to congenital hypothyroidism and irreversible mental retardation, making it the most common preventable cause of mental retardation. There is suggestion that maternal malnutrition (of macronutrient as well as micro nutrients) has adverse effect on birth weight and child development. Studies from developing countries suggest that nutrition supplements including multiple micronutrient supplements have positive impact on birth weight as well as child development. It has been shown that the overall quality of maternal care can produce lasting changes in stress reactivity, anxiety and memory in the child. Various drugs and toxins such as maternal drug or alcohol abuse, antiepileptic drugs and environmental toxins can have adverse effect on child development. Pregnancy induced hypertension, hypothyroidism, malnutrition and fe to placental insufficiency due to any cause.
It is estimated that by the time of diagnosis of diabetes treatment pink eye cheap topiramate online visa, patients have lost nearly 50% of their beta-cell mass. With loss of beta-cell mass, insulin secretion is no longer sufficient to compensate for insulin resistance, defined as a subnormal response to a given insulin concentration. Elevated fasting or postprandial insulin values are the hallmark of insulin resistance, which is often associated with obesity; weight reduction may improve insulin sensitivity. The lower prevalence of type 1 diabetes has made determining who is at risk more difficult. Identifying people in the prediabetic phase of type 1 diabetes requires serial measurements of beta-cell function and close monitoring of immunologic markers, making selection of an appropriate cohort difficult. However, neither study demonstrated effective prevention of progression to type 1 diabetes. The gold standards for defining insulin resistance are the intravenous glucose tolerance test, insulin suppression test, and euglycemic insulin clamp. It is estimated that at the time of diagnosis, patients with type 2 diabetes have lost nearly 50% of their insulin-producing cells. The system of programmed beta-cell death (apoptosis) occurs progressively over the course of type 2 diabetes and has many potential triggers, although two specific possibilities have been characterized. Both of these conditions have been amply described in subjects with either prediabetes or overt diabetes and clearly contribute to the genesis of type 2 diabetes by reducing the number of functioning beta cells. Both recommend that patients have a complete history and physical examination at the initial visit. Laboratory testing should include a fasting lipid profile and measurement of HbA1C. Surveillance for complications should include an annual physical examination, ophthalmologic examination, and a screen for microalbuminuria. Overall glycemic control (HbA1C) should be assessed at least semiannually in all patients and quarterly in insulin-treated patients and in patients with poorly controlled type 2 diabetes. Diabetes is a self-management illness and requires that the patient be educated in glucose selfmonitoring, nutrition therapy, exercise, and the proper use of medications. Because patients with type 1 diabetes are completely insulin deficient, the medical regimen is straightforward and centered on insulin replacement. The most physiologic replacement regimen, known as the basal-bolus technique, can be accomplished either with the use of a long-acting (basal) insulin in combination with a rapid-acting (bolus) insulin or a continuous subcutaneous infusion using an insulin pump. After an average 17 years of follow-up, the intensively treated cohort also enjoyed an approximate 50% reduction in cardiovascular risk. The only major adverse effect of intensified control was a threefold higher risk of severe hypoglycemia. An intensive therapy regimen requires blood glucose monitoring four to eight times daily with multiple daily insulin injections or an insulin pump and is best managed by a team comprising a physician, certified diabetes educator, nurse, and dietitian. The potential reduction in cost for treating diabetic complications (laser photocoagulation, dialysis, kidney transplants, hospitalizations, and rehabilitation following amputations) has been shown to justify the cost of personnel and supplies for intensive therapy. The risk-to-benefit ratio for intensive therapy may be less favorable for prepubertal children, patients with advanced complications, and patients with coronary or cerebrovascular disease. Investigators recruited 5102 patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes in 23 centers within the United Kingdom between 1977 and 1991. Patients were followed up for an average of 10 years to determine the impact of intensive therapy using pharmacologic agents in comparison with dietary therapy alone. The study also tested the relative efficacy of intensive (tight) blood pressure control and "less tight blood pressure control. Tight blood pressure control was associated with a reduction in both microvascular and macrovascular events. When the entire cohort of patients was studied together, the mean HbA1C level for the duration of the study was a strong positive predictor of all diabetes-related end points, including death, amputation, myocardial infarction, and stroke. The benefits of early glucose and blood pressure control in reducing the both the microvascular and macrovascular complications and all-cause mortality persisted 10 years after the end of the original trial. The foundation of therapy is diet, exercise, and patient education; unless there are contraindications to its use, metformin should be started at the time of diagnosis. The next steps may involve additional oral agents or injectable medications, and all further treatment decisions must consider the individual characteristics of the patient as well as comorbidities.
In the meta-analysis symptoms 3 weeks into pregnancy order topiramate toronto, hyperlipidemia improved in 70% or more of the patients, hypertension resolved in 62% and resolved or improved in 79% of patients, and obstructive sleep apnea resolved in 86%. Hypertension improves in many patients but is more resistant to improvement than diabetes or sleep apnea. Common causes of death among patients undergoing bariatric surgery included pulmonary embolism and anastomotic leaks. Stomal stenosis or marginal ulcers (occurring in 5% to 15% of patients) present as prolonged nausea and vomiting after eating or inability to advance the diet to solid foods. These complications are treated by endoscopic balloon dilatation and acid suppression therapy, respectively. To prevent dumping syndrome, patients should be encouraged to consume frequent, small meals and to avoid fruit juices and added sugars. Unlike patients with insulinomas, these patients often experience severe hypoglycemia following the ingestion of carbohydrates. Initial descriptions emphasized the presence of nesidioblastosis, or beta-cell hyperplasia as a cause and demonstrated the value of partial pancreatectomy as a treatment in severe cases. More recently, studies have suggested that most patients with this syndrome can be treated by modifying the diet to include less carbohydrate and increasing the consumption of slowly absorbed (low glycemic index) carbohydrates in the context of mixed meals. While dietary carbohydrate restriction is the principal treatment for hypoglycemia following gastric bypass surgery, a number of medications have been found to be of use including acarbose, calcium channel blockers, diazoxide, and octreotide. By bypassing the stomach, duodenum, and varying portions of the jejunum and ileum, malabsorption of thiamine, iron, folate, vitamin B12, calcium, and vitamin D may occur. In general, the greater the degree of malabsorption, the higher the risk of nutritional deficiencies. To prevent deficiencies, patients should routinely be discharged from the hospital with daily vitamin and mineral supplementation that contains between 1. The following laboratory tests should be performed preoperatively and at 6-month intervals for the first 2 years, followed by annual assessments thereafter: complete blood count, comprehensive metabolic panel, lipid panel, and measurements of hemoglobin A1C (for diabetic patients), ferritin, folate, vitamin B12, 25-hydroxy vitamin D, and parathyroid hormone. With more extensive procedures, such as biliopancreatic diversion, protein malnutrition and deficiencies of the fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, and K) may occur. Some patients in whom iron deficiency anemia develops following weight loss surgery require treatment with parenteral iron. With judicious monitoring and adequate supplementation, all of these deficiencies are largely avoidable and treatable. Hession M, Rolland C, Kulkarni U, et al: Systematic review of randomized controlled trials of low-carbohydrate vs. National Institutes of Health: the practical guide to the identification, evaluation and treatment of overweight and obesity in adults, Obesity Res 6:(Suppl 12), 1998. Fragility fractures are fractures that occur spontaneously or following minimal trauma, defined as falling from a standing height or less. Fractures of the vertebrae, hips, and distal radius (Colles fracture) are the most characteristic fragility fractures, but patients with osteoporosis are prone to all types of fractures. Approximately one third of all vertebral fractures are painful, but two thirds are asymptomatic. Hip fractures are associated with permanent disability in nearly 50% of patients and with a 20% higher mortality rate than in the age-matched population without fractures. Central densitometry measurements (spine and hip) are the best predictors of fracture risk and have the best precision for longitudinal monitoring. Peripheral densitometry measurements (heel, radius, hands) are more widely available and less expensive. Osteoporosis should be diagnosed in any patient who sustains a fragility fracture.
Syndromes
Another key question is the role of revascularization in patients with moderate to 12 - Which Therapy for Which Condition These results are consistent with almost 3 decades of trials and emphasize that current mortality rates in patients with chronic stable angina on intensive medical therapy receiving aggressive secondary prevention are low and unlikely to be improved by revascularization medications zetia buy 100mg topiramate with visa. Third-generation stents are under development and may further change the landscape. This is an area of continued investigation and evaluation,47 with special reference to cognitive function,48 graft patency,49 and mortality. Furthermore, stent insertion has become more adventurous; for example, multiple stent insertion is common and selected stenting 12 - Which Therapy for Which Condition Revascularization is the key when the effort angina is more than mild, especially if symptoms are escalating. The patient population with refractory angina not amenable to revascularization is growing and constitutes a difficult clinical problem. Alternative therapies such as chelation and acupuncture, ineffective in controlled trials, should be avoided. Those at high risk are given ticagrelor or clopidogrel, and taken to the catheter laboratory. Morphine sulfate is given intravenously if the pain persists or if the patient is agitated or pulmonary congestion is present. In fact, a recent systematic review suggested a trend toward harm from the administration of oxygen, but this could be due to chance. Aspirin on arrival or before, continue indefinitely (class 1A), nonenteric 162-325 mg; long-term 75-162 mg daily, higher disease after stenting. If aspirin intolerant, clopidogrel loading dose 300 mg, then 75 mg daily (class 1A). Proton pump inhibition if gastric intolerance to aspirin or clopidogrel (class 1B). In patients who are unable to take aspirin, the case for clopidogrel is self-evident. Current evidence suggests that clopidogrel responsiveness is a clinically relevant factor, but we are not sure how to deal with this therapeutically. This has led to the development of growth that has higher efficacy but more bleeding. Its antiplatelet inhibiting effects appear greater than with clopidogrel, but it is not yet approved for clinical use. This allows for a longer period of treatment and consequently offers some protection against the "rebound" phenomenon seen soon after heparin withdrawal. Because there are no direct head-to-head comparative trials, definitive conclusions cannot be drawn. Not only is the complication rate increased, but in some studies, overall mortality was higher. Arguments for b-blockade largely rest on first principles (reduced myocardial demand). For higher-risk patients or those with ongoing rest pain, intravenous b-blockers are followed by oral administration, whereas oral b-blockers will suffice for patients at lower risk. Diltiazem compared well with nitrates during the acute phase of unstable angina, with better event-free survival at 1 year. Note major role of anticoagulants, including fondaparinux and antiplatelet agents (aspirin plus clopidogrel). Calcium channel blockers such as diltiazem (heart-rate lowering) may be used intravenously or orally if b-blockade is contraindicated or fails or with care added to b-blockade. Dihydropyridines such as amlodipine and nifedipine should generally not be used unless vasospastic angina is strongly suspected. In patients with refractory angina on maximal medical therapy, the potential antiarrhythmic effects of ranolazine are currently under investigation. The former involves coronary angiography with a view toward coronary 476 12 - Which Therapy for Which Condition Clopidogrel is chosen in those who are intolerant to aspirin, and in some patients is added to aspirin. The Mediterranean diet has strong support, especially because it reduced total mortality (see p. Other risk factors also need optimizing, including weight loss, increased exercise, and smoking cessation. Longterm b-blockade is generally recommended, although without firm supporting contemporary trial data, and with potential side effects of fatigue, erectile dysfunction, and weight gain that mitigate against an optimal lifestyle. Short-acting nifedipine, diltiazem, and verapamil all completely abolish the recurrence of angina in approximately 70% of patients, with a substantial improvement in another 20%. Order 100mg topiramate visa. Atlas Genius - Back Seat (Bing Lounge).
|