Zetamax"Generic 250 mg zetamax with mastercard, antibiotics for acne nausea". By: Y. Aila, M.B. B.CH., M.B.B.Ch., Ph.D. Associate Professor, New York University School of Medicine Vitamin B12 should be supplemented parenterally in patients who have extensive ileal disease or an ileal resection infection viral cheap 250 mg zetamax otc. Patients taking corticosteroids require supplemental calcium and vitamin D, and individuals with extensive small bowel involvement can also develop malabsorption of fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, and K), iron, and, rarely, trace minerals. Lactose-free diets and lowfiber diets may be necessary in patients with active disease or strictures. SurgicalManagement Surgical intervention is indicated for patients with severe complications such as obstruction, perforation, massive gastrointestinal hemorrhage, or toxic megacolon not responsive to medical treatment. The other main indication for surgical treatment is the presence of dysplasia or cancer. In this operation, the colon is removed and the small bowel is constructed into a reservoir (ileal pouch) that is anastomosed to the anus, allowing defecation through the anus. Complications include the development of pouchitis, fecal incontinence, reduced fertility, and need for reoperation. Only 5% of individuals with proctitis undergo colectomy by 10 years after diagnosis. The colon cancer risk is increased 10- to 20-fold after 8 to 10 years of disease in pancolitis, and after 15 to 20 years in left-sided colitis. It is the leading cause of hospitalization of patients with gastrointestinal disorders in the United States, with more than 200,000 admissions annually. This translates into an overall incidence of 1 case per 4000 people in the general population. Normal physiology involves secretion of inactive enzymes into the duodenum, where they are converted to an active form by enterokinase, a brush border enzyme secreted by small bowel enterocytes. Based on experimental models, the initiating event appears to involve intra-acinar activation of trypsin from trypsinogen, resulting in acute intracellular injury, pancreatic autodigestion, and the potential for profound systemic complications after activated enzymes are leaked into the bloodstream. During the initial hospitalization for acute pancreatitis, reasonable attempts to determine the cause are appropriate, particularly those that may affect acute management. The cause of acute pancreatitis is readily identified in 70% to 90% of patients after an initial evaluation consisting of the history, physical examination, focused laboratory testing, and routine radiologic studies. Gallstones account for 45%, alcohol for 35%, miscellaneous causes for 10%, and idiopathic causes for 10% to 20% of acute pancreatitis cases Table 38-1). Gallstone Pancreatitis Among patients with gallstones, the incidence of acute pancreatitis is 0. It is theorized that gallstone passage causes transient obstruction of the pancreatic duct, precipitating acute pancreatitis. Most stones pass spontaneously from the ampulla and do not require intervention (discussed later). Alcoholic Pancreatitis Acute alcoholic pancreatitis is the second most common cause of pancreatitis in the United States. Approximately 10% of chronic alcoholics develop attacks of pancreatitis that are indistinguishable from other forms of acute pancreatitis. As an exocrine gland, the pancreas participates in normal digestion and nutrient absorption. Within acinar cells, proteolytic digestive enzymes are synthesized and packaged separately in the Golgi region into condensing vacuoles and transported in an inactive form referred to as zymogens to the apical portions of the cell. When stimulated, they are discharged into the central ductule of the acinus by exocytosis. In the Undergraduate teaching project in gastroenterology and liver disease, unit 24, Bethesda, Md. Acinar cell injury and necrosis; release and activation of digestive enzymes and cell proteins 1. Activation of digestive juices proteolytic, lipolytic, or other enzymes in interstices of pancreas 4. However, some have true acute alcoholic pancreatitis because not all patients progress to chronic pancreatitis, even with continued alcohol abuse. The mechanism of pancreatic injury, the genetic and environmental factors that influence its development in alcoholics, and the reason only a small proportion of alcoholics develop pancreatitis are unclear (see Chronic Pancreatitis). Diagnosis of these genetic disorders contributes little to direct management because specific therapy is unavailable. However, identification of an underlying genetic cause may obviate the need for further testing, allow more informed family planning, and enable better surveillance for complications, including pancreatic cancer. The decision to pursue genetic testing is one that should be made only with the advice and involvement of an experienced counselor.
If an animal bite has occurred antibiotics for uti caused by e coli proven zetamax 250mg, the timing of the bite, circumstances of injury, and health status of the animal should be determined. Initial antimicrobial management, if indicated, is directed by the history and physical examination findings. Evaluation of hospitalized patients should include a complete blood count and a basic metabolic panel. The C-reactive protein level may be useful as a marker for inflammation and guidance for treatment. The creatine phosphokinase concentration may be helpful, but it is not specific for cases of compartment syndrome and necrotizing fasciitis involving the musculature. The benefit of blood cultures for cellulitis in hospitalized patients is uncertain because the yield is low. Cultures are indicated for patients who require incision and drainage because of the risk of deep structure and underlying tissue involvement. Human Bites Wounds swabs may produce misleading information in cases of human bites. Group A streptococci Treponema pallidum, Haemophilus ducreyi, Sporothrix, Bacillus anthracis, Francisella tularensis, Mycobacterium ulcerans, Mycobacterium marinum Corynebacterium diphtheriae Group A or other streptococci, S. If feasible, tissue biopsy or aspiration of the infected site can provide specimens for aerobic and anaerobic culture. Analysis of initial cultures should focus on common pathogens, and additional testing should be reserved for uncommon or rare infections associated with unusual circumstances, such as Vibrio species after salt water exposure. Tissue biopsy and special stains may be required in certain situations, such as suspected infection with M. Burn Wounds Before sampling, the burn area must be clean and devoid of topical antimicrobial agents. Surface swabs or tissue biopsies are recommended for obtaining culture samples, and histopathologic examination can monitor for the presence and extent of infection. Quantitative evaluation of swab or culture specimens is recommended twice weekly to monitor colonization. Diabetic Foot Infections Superficial swab cultures of ulcerations can be misleading and should be avoided. Chapter 87 discusses the laboratory diagnosis of infectious diseases in more detail. Severe cellulitis should be managed with parenteral cefazolin, nafcillin, or oxacillin. Concomitant tinea infection should be treated with a topical antifungal agent such as clotrimazole or terbinafine. Severe cases requiring parenteral antibiotics require vancomycin, daptomycin, telavancin, ceftaroline, clindamycin, or linezolid. In addition to supportive care, urgent surgical consultation should be obtained in the event that crepitus, bullae, rapidly evolving cellulitis, or pain disproportional to physical examination findings suggests necrotizing fasciitis. Initial parenteral therapy with vancomycin, daptomycin, linezolid with piperacillintazobactam, cefepime plus metronidazole, or a carbapenem is appropriate. The use of intravenous immune globulin in cases of necrotizing fasciitis remains controversial. Compartment syndrome requires emergent surgical decompression to prevent muscle necrosis and irreversible neuronal damage. For patients with a penicillin allergy, a fluoroquinolone plus clindamycin or sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim plus metronidazole are alternatives that may be used in oral or parenteral forms. Inpatient parenteral agents including ampicillinsulbactam or piperacillin-tazobactam may be used for patients who are not allergic to penicillin. Tularemia is treated with gentamicin, tobramycin, streptomycin, doxycycline, or ciprofloxacin.
Although young and pregnant patients are often not treated until they become symptomatic antimicrobial effects of spices order 250 mg zetamax with visa, older patients (>60 years) and those with a history of thrombosis, long disease duration, or significant cardiovascular risk factors are likely to benefit from the addition of platelet-lowering agents. Hydroxyurea, an oral cytotoxic, myelosuppressive agent, is the most common first-line agent, and it usually is well tolerated and has low long-term leukemogenic risks. Although the median age at diagnosis is 60 to 65 years, 10% to 25% of patients are younger than 40 years. Vasomotor symptoms include headache, dizziness, visual changes, and erythromelalgia. Serious arterial thrombotic complications such as transient ischemic attacks, strokes, seizures, angina, and myocardial infarctions may occur. Megakaryocyte proliferation with large and mature morphology; no or little granulocytic or erythroid proliferation 3. Chronic myeloproliferative disorders: chronic idiopathic myelofibrosis, chronic myelogenous leukemia, polycythemia vera b. Granulomatous diseases: mycobacterial infections, fungal infections, sarcoidosis b. Pathology An abnormal myeloid precursor is thought to give rise to dysplastic megakaryocytes that produce increased levels of angiogenic and fibroblast growth factors. These cytokines act on normal fibroblasts and other stromal cells, a process that stimulates excessive proliferation and collagen deposition. Over time, increasing fibrosis of the bone marrow leads to premature release of multipotent hematopoietic precursors into the periphery. These cells then migrate and reestablish themselves in other sites, thereby shifting hematopoiesis out of the bone marrow and into other tissues, especially the spleen and liver. Megakaryocyte proliferation and atypia accompanied by reticulin and/or collagen fibrosis, or in the absence of reticulin fibrosis, the megakaryocytic changes must be accompanied by increased marrow cellularity, granulocytic proliferation, and often decreased erythropoiesis. Not meeting World Health Organization criteria for chronic myelogenous leukemia, polycythemia vera, myelodysplastic syndrome, or other myeloid neoplasm 3. Palpable splenomegaly *Diagnosis of primary myelofibrosis requires meeting all three major criteria and two minor criteria. Although low blood counts may occur, overall platelet and red blood cell numbers at diagnosis may be increased or normal depending on the degree of compensatory extramedullary hematopoiesis. Review of the peripheral blood profile commonly reveals leukoerythroblastic changes characterized by teardropshaped erythrocytes, giant platelets, and nonleukemic immature myeloid, erythroid, and leukocyte cells. Other underlying causes of neoplastic and non-neoplastic bone marrow fibrosis Table 46-5) should be ruled out. As bone marrow failure evolves, complications of neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, and anemia develop as a result of ineffective hematopoiesis. ClinicalPresentation Although many patients are asymptomatic at diagnosis, most complain over time of progressive fatigue and dyspnea related to anemia or early satiety and left upper quadrant pain associated with splenomegaly and splenic infarction. More than one half of these patients develop massive hepatosplenomegaly due to extramedullary hematopoiesis. Other causes of nonleukemic death include heart failure, infection, intracranial hemorrhage, and pulmonary embolism. Symptoms caused by excess thrombocytosis and leukocytosis or progressive extramedullary hematopoiesis may be managed with hydroxyurea as a first-line agent or interferon- in younger or pregnant patients. Symptomatic splenomegaly is best managed with hydroxyurea because open splenectomy is associated with significant operative morbidity and mortality and splenic irradiation is poorly tolerated except as a palliative approach. Patients receiving ruxolitinib had significantly greater spleen volume reduction and symptom improvement. Updates from both trials have demonstrated significantly prolonged overall survival and improvements in bone marrow fibrosis in the ruxolitinib-treated patients compared with control arms. In contrast, the peripheral blood smear in reactive granulocytic hyperplastic states. Based on this study, imatinib was the first rationally designed biologically targeted drug approved for the treatment of cancer. However, whether these results translate into long-term overall survival benefit for either agent over imatinib remains to be seen. Buy cheap zetamax 500 mg online. First aid kits. Arguably virus c buy 250 mg zetamax otc, asbestos is the most common cause of occupational cancer because of its link with the development of mesothelioma and other types of lung cancer. A strong interaction exists between asbestos exposure and cigarette smoking leading to lung cancer. A range of medications are associated with increased cancer risk, including the alkylating agents, anthracyclines, and other classes of cancer chemotherapy agents and immunusuppressants. Estrogen use in postmenopausal women increases the risk of endometrial cancer; the rates drop when estrogen is combined with progesterone. Lifestyle exposures to carcinogenic chemicals include multiple carcinogens in tobacco products and dietary factors, including aflatoxins, in many parts of the world. LifestyleChanges Smoking cessation is unquestionably the most direct and effective cancer prevention strategy available. More than 1 million people die from tobacco-induced cancers globally each year, and tobacco accounts for one third of all cancer diagnoses in the United States. Although tobacco prevention and control programs have resulted in a decline in smoking prevalence in the United States, tobacco use continues to be high and has been increasing in a number of countries. There is also evidence from epidemiologic studies that other lifestyle changes, including regular exercise and dietary modification, may also reduce the risk of cancer. Central adiposity is associated with increased incidence of and mortality from a number of cancers, including breast and endometrial cancers. Sufficient dietary intake of fruits and vegetables appears to reduce the risk for gastric and esophageal cancers. Avoidance of excessive sun exposure and artificial tanning devices may reverse the recent upward trend in cutaneous malignancies. Reduction in exposures to known carcinogenic agents is an important goal in both occupational and domestic settings. Evidence for an association between air pollution and lung cancer incidence illustrates how difficult such reductions may be. However, limiting the use of potentially carcinogenic chemicals and of radiation in the medical setting is sensible. Cancer screening programs should detect premalignant states or early-stage cancers before the onset of symptoms with relatively high sensitivity. For cancer screening to be useful, there must be a treatment available that improves the outcome for patients with premalignant or early-stage disease. Ideally, such screening programs should also be noninvasive, inexpensive, and associated with high specificity. Identification of high-risk individuals assists in genetic counseling and testing as well as in cancer screening efforts. Proper interpretation of the results of cancer screening studies must consider both lead-time bias and length-time bias. Lead time is the time between detection of disease by screening and the actual appearance of symptomatic disease. If screening leads to early diagnosis, it may appear that the patient lived longer than would have been the case without screening even when the survival of the patient from the onset of disease has not been altered. Length-time bias occurs when subsets of the cancer under study have different growth rates. Screening is more likely to detect cancers that grow slowly because of the greater prevalence of asymptomatic people with slow-growing tumors than those with fast-growing tumors. Patients with cancer that is detected by screening may appear to have longer survival times as a result of screening when in fact the longer course of their disease results from the behavior of the tumor itself. Although randomized controlled trials of cancer screening programs require large numbers of participants and take years to complete, such trials are needed to quantitate the value of screening and to address both lead-time and length-time bias. Screening tests may also be associated with false-negative and false-positive results. False-negative results fail to identify a proper diagnosis and patients therefore are not provided the opportunity for effective early treatment.
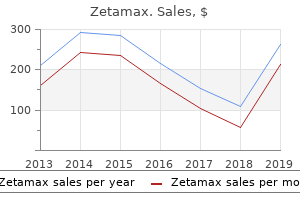
|