Betnovate"Betnovate 20 gm without prescription, acne before and after". By: W. Onatas, M.S., Ph.D. Vice Chair, Ohio University Heritage College of Osteopathic Medicine If a urethral injury is suspected acne los angeles betnovate 20gm low cost, one cautious attempt at catheterisation by an experienced doctor Investigation To diagnose bladder injuries a cystogram is the investigation of choice. Filling of the retrovesical space, paracolic gutters and outlining of intra-abdominal viscera are indicative of intraperitoneal rupture. This classically leads to a butterfly haematoma across the perineum, and extension of blood through the penis, scrotum and lower abdominal wall. This test is inappropriate in unstable patients who would benefit primarily from imageguided suprapubic catheter insertion. Bladder injuries associated with a normal cystogram are usually attributable to a peri-vesical haematoma and conservative management with catheter drainage alone is appropriate. Similarly, the majority of patients with an extraperitoneal rupture can be managed with a urethral catheter. The exceptions to this include patients with bladder neck or associated vaginal or rectal injuries and those undergoing operative repair of a pelvic fracture, particularly where a bony spicule penetrates the bladder. External penetrating injuries and blunt intraperitoneal bladder ruptures require formal surgical exploration and open repair. Absorbable sutures are mandatory in order to prevent subsequent bladder stones and it is generally advisable to leave both a suprapubic and urethral catheter. Management If a suprapubic catheter is required, this should be placed using a Seldinger technique under ultrasound guidance by a doctor experienced in the technique. A retrograde urethrogram (b) showing a posterior urethral injury with a leak of contrast medium from the membranous urethra. Indications for primary (within 48 hours) urethral repair are: associated anorectal injury, perineal degloving, bladder neck injury, massive bladder displacement and penetrating trauma to the anterior urethra. This complex surgery should be undertaken in a specialist centre by a surgeon specialising in reconstructive urology. Primary realignment of the urethra during fracture surgery is no longer recommended, as in the hands of an inexperienced surgeon the risk of additional damage probably outweighs the benefits. Accurate reduction of the bony pelvic ring indirectly realigns the urethra and facilitates delayed repair. Delayed repair should be carried out 3 months post-injury by a reconstructive urological surgeon. In trauma cases, check for blood at the urethral meatus; this is a sign of urethral injury. Despite the seemingly vulnerable position of the male genitalia within the scrotum, traumatic injury is relatively rare. Genital injury may have an effect on fertility and therefore requires urgent attention. Testicular trauma Testicular trauma may be categorised as blunt, penetrating or degloving. Blunt trauma to the testis can occur from a kick to the groin or from being struck by a hard object such as a cricket ball. Blunt injuries are more common (approximately 85%) than penetrating injuries and are frequently minor, often permitting a conservative management approach. Penetrating injury from sharp objects or gun shot typically require surgical exploration and treatment, and in these instances bilateral injury is much more common. Degloving refers to shearing of the scrotal skin and dartos muscle leaving the testes exposed. As mentioned acne xojane buy cheap betnovate 20 gm line, the 5-year survival rate refers to the number of patients still alive 5 years after diagnosis, whether they are disease-free, in remission, or under treatment. Unfortunately, this does not mean that 5-year survivors have been permanently cured of lung cancer. All types of smoking- cigarettes, cigars, and pipes-increase the risk for lung cancer. For example, there is a public health debate about whether screening smokers with X-rays or mucus samples saves lives. It is also chronic and progressive, affecting multiple systems, especially the lungs, digestive tract, and pancreas. This mucus clogs airways, causing breathing problems, bacterial infections, and lung damage. The disease occurs mostly in Whites whose ancestors came from northern Europe, although it does affect to a lesser degree all races and ethnic groups. It is the most common deadly inherited disease affecting Whites in the United States. A small number are not diagnosed until age 18 or older because older patients tend to have a milder form of the disease. Over time, mucus buildup and infections cause permanent lung damage, including scar tissue and cysts. With the thick buildup of mucus in the intestines and in the lungs, patients experience diarrhea, malnutrition, poor growth, weight loss, frequent respiratory infections, breathing difficulty, and eventually permanent lung damage. Other diagnostic tests include blood tests, chest X-rays, lung function tests, and sputum cultures. Ideally, gene therapy repairs or replaces the defective gene before symptoms cause permanent damage. However, these tests are expensive and carry risks for the mother, and are not used for all pregnant women. Lung Failure Lung failure, or respiratory failure, occurs when not enough oxygen passes from the lungs into the blood. Both of these problems, a dangerously low oxygen level and a dangerously high carbon dioxide level in the blood, can occur at the same time. For example, patients who have diseases or injuries that affect the muscles, nerves, bones, or tissues that support breathing are at risk. In severe cases, there is cyanosis, which is a bluish color to the skin, lips, and fingernails. Eventually, the brain and heart malfunction, resulting in severe drowsiness and abnormal heartbeats, both of which can lead to death. A health care provider detects lung failure based on symptoms and a physical examination. A blood test confirms the diagnosis when it shows a dangerously low level of oxygen or a dangerously high level of carbon dioxide. Chest X-rays and other diagnostic tests are done to determine the cause of lung failure. A goal to treating lung failure is to get oxygen to the lungs and other organs and to remove carbon dioxide from the body. By treating the underlying cause, the symptoms of lung failure can become less severe. Oxygen is given at first, usually more than is needed, but then the amount is adjusted over time. Patients with severe lung diseases need long-term breathing support, such as portable oxygen therapy. In the case of chronic lung failure, portable oxygen therapy takes the form of extra oxygen given through two small plastic tubes (cannula) that are placed in both nostrils or through a mask that fits over the nose and mouth. If the patient still has trouble breathing, then oxygen is given through a tracheostomy. This is a surgically opened hole that goes through the front of the neck and into the windpipe. There are three main parts to the respiratory system: airways, lungs, and muscles. Discount betnovate uk. PARABEN FREE SKIN CARE | Skincare Routine for All Skin Types | Skin Care for Glowing Flawless Skin.
Treatment options depend on symptoms acne 12 weeks pregnant buy betnovate 20gm overnight delivery, personal choices, medication side effects, and other factors. In some cases, a disorder can be so severe that a patient cannot make treatment decisions. If this is the case, the provider, family members, or loved ones may guide the treatment until the patient is able to make decisions. For those with a more serious disorder, a combination of treatments is the most effective. Medications for mental health disorders can be taken for a few days, a few years, or a lifetime, depending on the disorder. If there are side effects, then the provider changes the dose or switches to a different medication. Although medications do not cure a disorder, they can relieve symptoms and can also help make other treatments more effective. Antidepressants are the third most frequently taken medication of any kind in the United States, and it is estimated that up to 10% of the population takes antidepressants to relieve symptoms (National Institute of Mental Health, 2016b). Unfortunately, antipsychotics do not always make the symptoms go away completely, or forever. To stop symptoms from coming back, many patients need to take antipsychotic medication for the long term even if they feel better. Patients with a disorder sometimes do not want to take their medications; among other reasons, they may not like the side effects, or they may be in denial about their illness. The failure of patients with severe disorders to take medications is a serious and common problem with psychiatric care. It often leads to relapse of symptoms, rehospitalizations, homelessness, incarceration, victimization, or episodes of violence. Psychotherapy is a general term used to describe treatment based on patients talking about their personal issues with a therapist. During psychotherapy, patients learn about their moods, feelings, thoughts, and behavior. With the knowledge gained, patients then learn coping skills to deal with their disorder. The aim of therapy is to understand and express feelings, help change negative attitudes and behavior, and promote healthy ways of coping. As mentioned earlier, for many disorders, medication (to relieve symptoms) and psychotherapy (to help patients cope) are used together. There are different types of psychotherapy, including short term, long term, individual, and group. It can often be successfully completed in a few months, but in some cases, long-term treatment is needed. Brain stimulation therapies involve touching the brain directly with electricity, magnets, or implants to treat depression and other disorders. The patient is given an electric charge that is applied to the brain, causing a small seizure. Self-help groups are run by patients of the mental health care system or their families. These groups offer the chance to meet informally with other people who understand the same issues and challenges of dealing with a specific disorder. Sometimes a disorder is so severe that a patient needs care in a psychiatric hospital or a residential treatment program. These health care settings are recommended when patients cannot care for themselves or when they are in immediate danger of harming themselves or others. There are intensive outpatient treatment programs that offer ongoing mental health supervision, but the patient lives elsewhere. Most Americans with a disorder who receive treatment do recover and lead productive lives. It is unfortunate, however, that up to half of all people with disorders, and 90% of those who have a substance use disorder, do not get the treatment they need. Most disorders do not improve on their own; in fact, if left untreated, they may get worse over time and cause long-lasting problems. Hormonal replacement therapy after menopause is protective of disease activity in women with inflammatory bowel disease acne attack buy cheap betnovate 20 gm on line. Molecular biology of liver ischemia/reperfusion injury: established mechanisms and recent advancements. Better postresectional survival in female cirrhotic patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Characterization of the promoter region of human steroid sulfatase: a gene which escapes X inactivation. Spider angiomas in patients with liver cirrhosis: role of alcoholism and impaired liver function. Cellular-specific role of toll-like receptor 4 in hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice. Bioaccumulation of triclosan and triclocarban in plants grown in soils amended with municipal dewatered biosolids. Targeted disruption of the mouse estrogen sulfotransferase gene reveals a role of estrogen metabolism in intracrine and paracrine estrogen regulation. Comparison of the mortality and inflammatory response of two models of sepsis: lipopolysaccharide vs. Cloning and expression of the mouse pseudoautosomal steroid sulphatase gene (Sts). The protective effects of 17beta-estradiol on hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury in rat model, associated with regulation of heat-shock protein expression. Protective role of testosterone in ischemia-reperfusion-induced acute kidney injury. Spontaneous fetal loss caused by placental thrombosis in estrogen sulfotransferase-deficient mice. Clinical spectrum of steroid sulfatase deficiency: X-linked recessive ichthyosis, birth complications and cryptorchidism. Genetic background conditions the effect of sex steroids on the inflammatory response during endotoxic shock. Impaired Cd14 and Cd36 expression, bacterial clearance, and Toll-like receptor 4-Myd88 signaling in caveolin-1-deleted macrophages and mice. The human Xlinked steroid sulfatase gene and a Y-encoded pseudogene: evidence for an inversion of the Y chromosome during primate evolution. Liver ischemia and reperfusion injury: new insights into mechanisms of innate-adaptive immune-mediated tissue inflammation. In vivo modulation of murine serum tumour necrosis factor and interleukin-6 levels during endotoxemia by oestrogen agonists and antagonists. More recent research has uncovered interesting endobiotic functions of these xenobiotic receptors, including their regulation of the energy metabolism and energy homeostasis. Meanwhile, disruptions of energy homeostasis, such as type 2 diabetes and obesity, have an impact on drug metabolism. Although in most cases, biotransformations of xenobiotics lead to pharmacologically inactive metabolites, they may also activate so-called prodrugs to pharmacologically active products or even to toxic metabolites (Handschin and Meyer, 2003). However, the molecular basis underlying this drug-induced metabolism remained largely unknown for a long time. The plausibility of this hypothesis took a great leap forward with the discovery of the dioxin receptor or the AhR in 1976 (Poland et al. The evidence that AhR null mice showed impairment in the normal development of the liver, immune system, heart, and vascular tissues suggested the existence of endogenous AhR ligands as well as the physiological functions of AhR beyond mediating xenobiotic metabolism (Denison and Nagy, 2003; Fernandez-Salguero et al. They are expressed predominantly in the liver and small intestine where their target genes are located and are capable of binding to a wide variety of structurally diverse chemicals including endogenous and synthetic steroids, pharmaceutical agents, and xenobiotic chemicals. Given the dramatically increased number of patients suffering from metabolic syndrome such as steatosis, obesity, and diabetes, it is of great value to understand the impact of energy disturbance on the pharmacokinetics and efficacy of drug therapy. Steatosis may arise from an imbalance between triglyceride acquisition and removal due to increased fatty acid synthesis and uptake, decreased fatty acid b-oxidation, and reduced triglyceride secretion.
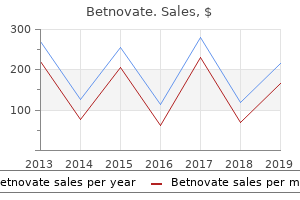
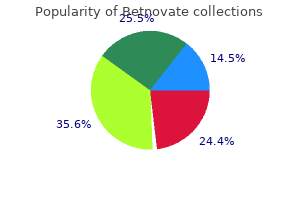
|